
How to Verify File Integrity After Successfully Accessing a RAR Archive
You’ve finally managed to open that important RAR archive — a project handover, historic backup, or sensitive corporate dataset. The password worked, the files extracted, and everyone is relieved. But there is still one crucial question: can you really trust what came out? If the archive was damaged in storage, partially restored from a failing disk, or handled through risky tools in the past, its contents might not be fully intact even though extraction “succeeded.”
This guide focuses on the stage after you legitimately access your own archive. It explains how to check whether extracted data is complete, authentic, and uncorrupted using safe, repeatable methods that fit into corporate workflows and personal best practices. We’ll look at basic visual checks, metadata analysis, hashes and signatures, and long-term strategies for keeping your data trustworthy — all while staying within legal and ethical boundaries for working only with files you own or are authorized to manage.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📌 TL;DR — What Integrity Verification Really Means After Extraction
In short: successfully opening your own RAR archive and extracting files does not automatically guarantee that the contents are complete, authentic, or uncorrupted. Drives fail, archives get partially damaged, and risky tools can alter data on the way in or out.
To protect yourself or your organization, treat extraction as step one and integrity verification as step two. At a minimum, you should:
- Check basic structure: do file counts, folder names, and timestamps look plausible for this project?
- Open and sanity-check key files: can important documents, images, or databases be read without errors?
- Compare to expectations: if you have old manifests, logs, or documentation, make sure everything that should be there is actually present.
- Use hashes and signatures where possible: compare checksums or digital signatures with known-good references.
- Document results: for corporate workflows, record what was checked and any discrepancies.
Doing this within a privacy-first, offline workflow keeps sensitive material away from untrusted online tools and makes it easier to prove that you handled data responsibly. Integrity verification becomes part of your standard process, not an emergency improvisation when something looks wrong.
🧠 Why File Integrity Checks Matter After Opening a RAR Archive
Many users assume that if WinRAR or another tool extracts files without an obvious error message, everything is fine. Unfortunately, that’s not always true. Subtle corruption can slip through, especially when archives have been copied between devices, stored on aging media, or partially repaired after incidents.
There are several reasons to take integrity seriously:
- Silent corruption: some file types will open but contain incorrect or missing data (for example, truncated logs or incomplete media files).
- Operational risk: using corrupted data in production can cause downstream issues, from wrong reports to failing imports.
- Compliance and audits: in regulated environments, you may need to show that recovered or restored data was validated before reuse.
- Security and tampering concerns: if archives have moved across untrusted systems, you may need to confirm nothing was altered.
A good starting point is to follow safe extraction practices for your RAR archives ↗️, then treat integrity checks as an extension of that discipline. You are not just opening files; you are deciding whether they can be trusted as evidence, project history, or active working data.
⚠️ Typical Risks After Extraction: Corruption, Tampering, and Partial Data
To design effective checks, you need to know what can go wrong. Common risks after accessing your own RAR archive include:
- Archived corruption: the RAR file itself may have been damaged by storage issues, power loss, or unsafe transfers. Even if extraction completes, some internal segments may be broken.
- Partial archives: multi-volume sets or incomplete downloads can produce a directory tree that looks correct but is missing actual content.
- Past “repairs” gone wrong: automated or manual attempts to “fix” a damaged archive may have discarded some content while making the file openable.
- External tampering: if archives were stored on shared systems without proper controls, malicious or accidental edits are possible.
Recognizing these patterns is essential when you work with damaged or fragile material. Earlier stages of your workflow should align with guidance on how to stabilize your partially corrupted RAR file ↗️ and safe first steps for repairing damaged RAR contents ↗️. Once you finally succeed in opening the archive, the question shifts from “can I access it?” to “did I get everything I was supposed to get?”
💼 All-in-One Integrity & Recovery Workspace for RAR Archives
In real workflows, integrity checks can become messy: one tool is used for extraction, another for checksum calculations, another for repair attempts, and logs are scattered across systems. This fragmentation makes it hard to prove what happened and to repeat a safe process when a new incident appears.
FileBrio RAR Master is designed to pull these activities into a controlled, offline workspace where you handle only your own archives. Within the same environment you can:
- Inspect archive structure and metadata before extraction.
- Work with corrupted archives using controlled, non-destructive approaches.
- Coordinate extraction, verification, and follow-up actions in one place.
For teams and individuals who regularly manage protected archives, using a dedicated toolkit rather than a patchwork of utilities improves both safety and traceability. You can align your process with the broader FileBrio RAR Master features ↗️ overview and incorporate integrity checks into your internal documentation and training.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
🧪 Practical Integrity Checks: From Quick Visual Review to Metadata
Once your own archive has been opened and files extracted, start with basic, non-technical checks before moving to advanced methods:
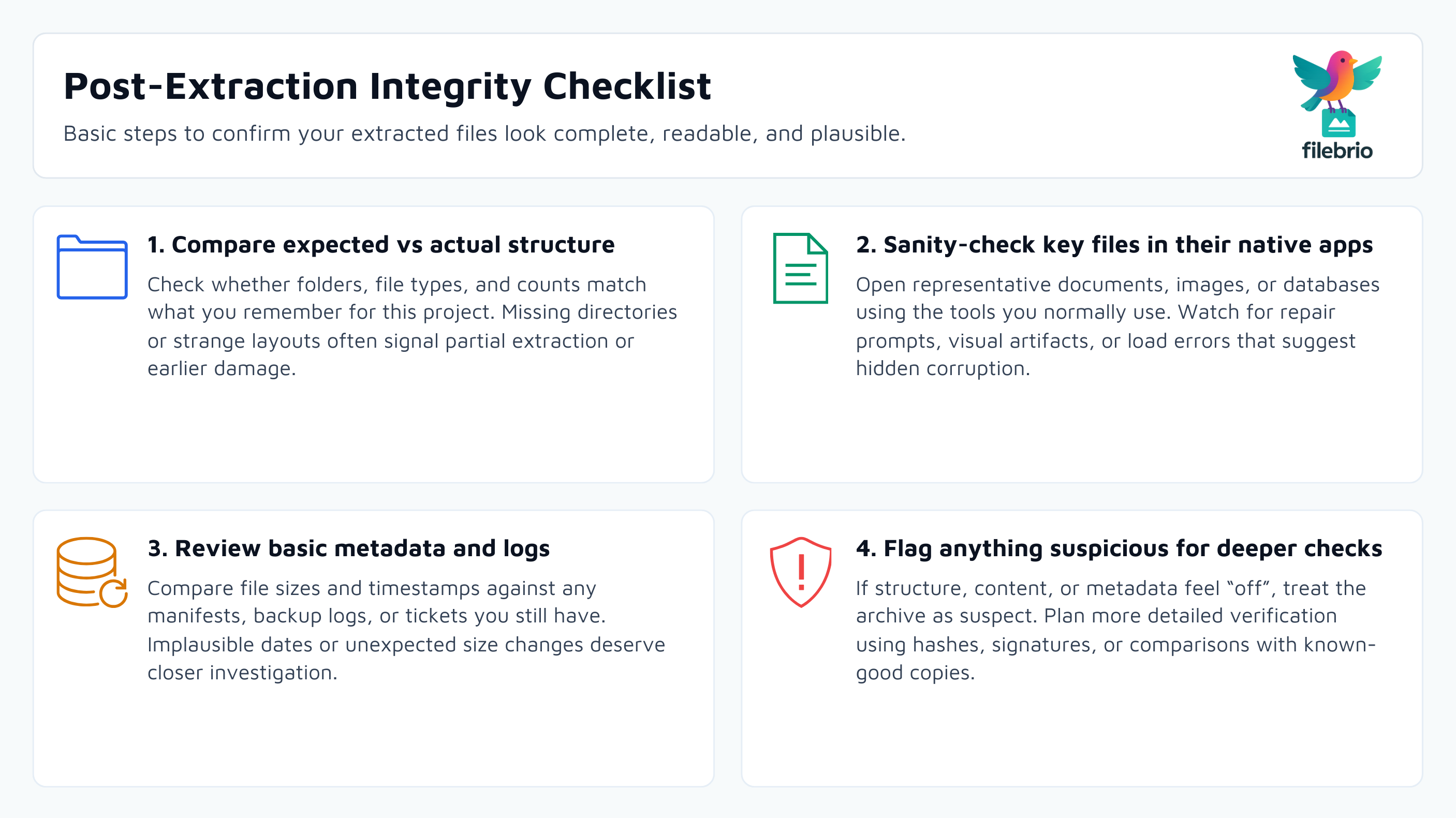
1. Compare Expected vs Actual Structure
Ask simple but important questions:
- Does the folder tree look familiar for this project or dataset?
- Are key directories or file types missing (for example, no “src/” folder where you expected one)?
- Do timestamps roughly match when the archive was created or last used?
When something feels “off,” treat it as a signal to dig deeper. Structured diagnostics similar to how to safely diagnose your locked RAR file ↗️ can be adapted to the post-extraction phase: instead of asking why the archive won’t open, you are asking why its contents don’t look as expected.
2. Open Representative Files
Open a sample of the most important files using the applications that normally handle them:
- Office documents: do they open cleanly, without repair prompts?
- Images: do they display without artifacts, color blocks, or truncated content?
- Databases or structured files: can they be read by your usual tools without errors?
This quick test often reveals obvious integrity issues early, especially when some internal data was lost or truncated during earlier corruption or repair events.
3. Review Basic Metadata and Logs
Where available, compare file sizes and timestamps against any manifests, backup logs, or project documentation you still have. For corporate archives, this might include ticket systems, change logs, or asset registers.
If you suspect deeper issues, reading archive metadata can help you understand what went wrong earlier in the lifecycle. Guidance on how to read RAR metadata to understand problems ↗️ and how to inspect internal RAR structure safely ↗️ is useful even after a successful extraction, because it helps you decide whether the original container may have left something out.
🔍 Hashes, Signatures, and Comparing Against Known-Good Copies
For higher assurance — especially in corporate, legal, or archival contexts — basic visual checks are not enough. You need objective evidence that extracted files match what they were at an earlier point in time.
1. Hashes and Checksums
If you have previously stored hashes (for example, SHA-256 values) for original files, you can recompute them after extraction and compare. Matching hashes strongly suggest that the contents are identical. Even without historic hashes, you can start storing them now for future verification.
In more mature programs, hash lists are kept alongside backup inventories and used whenever archives are restored. This practice pairs well with robust archive design that uses RAR recovery records and .rev volumes ↗️ to increase resilience: if recovery blocks help you restore a damaged archive, hashes help you confirm that restoration really brought the data back.
2. Digital Signatures and Authenticity
When data authenticity matters (for example, contracts, reports, or software builds), digital signatures or signed manifests are even stronger than hashes alone. A signature can prove that a file not only remained unchanged but also came from a specific key holder.
In corporate workflows, signatures are often part of a larger integrity pipeline linked to source control, build systems, and release processes. After extracting a RAR archive, verifying those signatures becomes a natural integrity step before the data re-enters production.
3. Comparing Against Known-Good Copies
Sometimes, the easiest check is to compare extracted files against an earlier copy that you still trust — for example, another backup, a deployed version of a project, or a verified snapshot.
If differences are detected, you can decide whether they are legitimate updates or signs of corruption. Where differences are suspicious and you suspect prior storage incidents, refer back to best practices for handling partially corrupted RAR files safely ↗️ rather than assuming the newest extraction is always correct.

🛡️ Secure Offline Tooling for Integrity Validation and Recovery
All of these checks should happen in an environment that respects privacy and compliance. Uploading sensitive archives or extracted data to online “checkers” or generic tools can create more risk than it solves.
Using a dedicated, offline-focused toolkit such as FileBrio RAR Master helps keep both the archive and its contents under your control. Integrity-focused workflows can combine:
- Safe extraction and re-extraction for testing scenarios.
- Integration with checksum and metadata analysis tools.
- Targeted repair attempts when archives show minor damage.
When corruption is detected, specialized capabilities like the corrupted archive repair feature ↗️ can be used to try to stabilize your own damaged RAR files before you rely on their contents. After repair, you repeat integrity checks so that you know which files were fully recovered and which may still be compromised.
For formal environments, it is also important to align your internal procedures with the vendor’s support and responsible use policy ↗️. This ensures that your workflows remain within legal and ethical boundaries, especially when archives contain regulated or sensitive information. Installation and updating of toolsets should follow your normal software governance, using the official FileBrio Office Suite download page ↗️ so administrators know exactly what is deployed.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
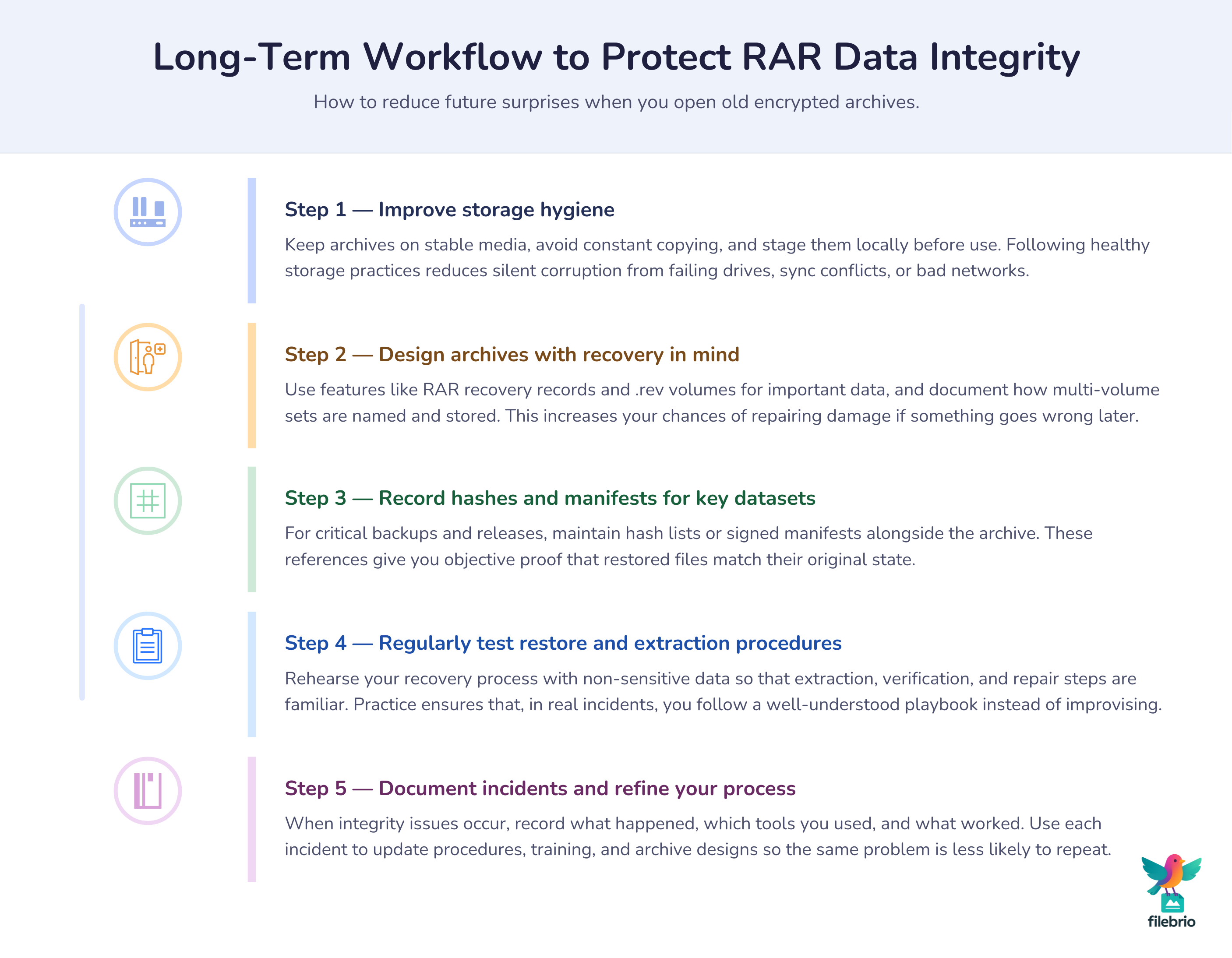
📈 Long-Term Protection: Preventing Future Integrity Surprises
Integrity verification is not just a one-time event after a tricky recovery. It should feed into your long-term protection strategy so that future extractions are less stressful and more predictable.
Key long-term measures include:
- Healthier storage habits: follow guidance on preventing RAR data loss on storage devices ↗️ so archives are less likely to become corrupted in the first place.
- Safe handling of large archives: for big backups or long-term collections, adopt best practices for managing large RAR archives safely ↗️ to reduce the impact of partial failures.
- Format and encryption awareness: understand how RAR4 and RAR5 encryption protect your data ↗️, and choose settings that match your security and integrity needs.
- Clear incident procedures: when error messages appear during extraction, follow processes informed by what to do when WinRAR shows “unexpected end of archive” ↗️ rather than improvising.
Finally, regularly test your own restore and extraction processes using non-sensitive data. This lets you rehearse integrity checks and refine your approach before you are forced to respond under pressure. Over time, integrity verification becomes part of your normal workflow, supported by diagnostics such as how RAR recovery records and .rev volumes protect data ↗️ and initial staging guided by how to safely diagnose inaccessible archives ↗️. The result is a more resilient, predictable environment where “we extracted it” always goes hand in hand with “and we know it’s intact.”
⚖️ Legal Reminder and Responsible Use
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
🔗 See Also: Related RAR Integrity and Safety Guides
- How to Confirm Whether Your RAR Archive Is Still Technically Recoverable ↗️
- What to Do When WinRAR Shows “Unexpected End of Archive” — Meaning and Safe Actions ↗️
- Understanding RAR Error Messages: What They Mean and How to Respond Safely ↗️
- How File-Type Structure Affects RAR Diagnostics and Feasibility Analysis ↗️
- How RAR Recovery Volumes (.rev) Help Reconstruct Missing Data ↗️
- How to Handle Damaged or Partially Corrupted RAR Archives Without Losing More Data ↗️
- Unzipping or Unrarring RAR Files (With or Without Password): Safe Extraction Practices ↗️