
How to Safely Store RAR Password Metadata for Future Access
You finally open an old RAR or WinRAR archive and feel a wave of relief — then you realize you have dozens more with similar passwords, scattered across drives, laptops, and cloud folders. You know that if you lose those passwords, modern encryption will not forgive you, and “reset links” or easy overrides simply do not exist.
That is exactly where RAR password metadata becomes critical. Instead of trying to remember every single password perfectly, you maintain a safe layer of hints, context, and structure that future you (or your team) can rely on years from now. Done right, this metadata helps you keep long-term access to your own archives without ever storing raw passwords in risky places.
This article explains what counts as RAR password metadata, what should never be written down, where and how to store it, how teams can share it responsibly, and how an offline toolkit like FileBrio RAR Master fits into a long-term access strategy that respects both security and usability.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📌 TL;DR — Why RAR Password Metadata Is Your Long-Term Safety Net
Short version: modern RAR and WinRAR encryption is designed so that if you lose a strong password, nobody can “reset” it for you. Instead of trying to remember every password perfectly, you should maintain password metadata — carefully chosen hints, descriptions, and context that future you can rely on to reconstruct or validate the right password without exposing it in plain text.
Good metadata might include where the archive came from, what project it belongs to, which password family you used, or the pattern (length, structure, ideas) behind the password. It should not include the full password itself in a readable form, and it should avoid details that would make it easy for others to guess it. Think of metadata as an index that reminds you how you were thinking when you created the password, not a cheat sheet that gives it away.
To use metadata safely, you need:
- A clear idea of what to record and what to avoid (no raw passwords in plain text).
- Reliable storage locations that are backed up, access-controlled, and resilient to device loss.
- Consistent habits so every new encrypted archive gets the same level of documentation.
- Offline, privacy-first tools that help you analyze archives and verify that your documentation still matches reality over the years.
Handled this way, RAR password metadata becomes your long-term safety net: you keep strong protection for your archives while giving future you a realistic path to legitimate access — without ever weakening the encryption model itself.
🧠 Why Password Metadata Matters More Than You Think
RAR encryption is intentionally unforgiving: if you forget a sufficiently strong password, there is no support hotline that can reset it. Articles explaining how encryption controls access to your protected RAR contents ↗️ emphasize this point — your password is the gatekeeper, and the encryption system is designed to obey it faithfully, not override it.
At the same time, modern formats such as RAR5 strengthen this model even further. They use stronger ciphers and heavier key-derivation functions, as described in resources like how RAR4 and RAR5 secure your protected data ↗️. These changes are excellent for privacy, but they also make “just try all options” increasingly unrealistic once passwords become long and complex.
That is why password metadata is not an optional extra; it is a practical necessity. Properly managed metadata:
- Preserves your future options. Even if you do not remember the exact password, you remember how you were thinking when you created it.
- Reduces panic-driven decisions. When you hit a locked archive years later, you have written context, not just anxiety.
- Supports structured diagnostics. You can align what you know about the password with what archive analysis tools show you.
Thoughtful metadata also integrates into your broader strategy for how to reinforce protection of your encrypted RAR files ↗️. Instead of choosing between “strong but forgettable” or “weak but memorable,” you design a system where strong passwords are supported by strong documentation.
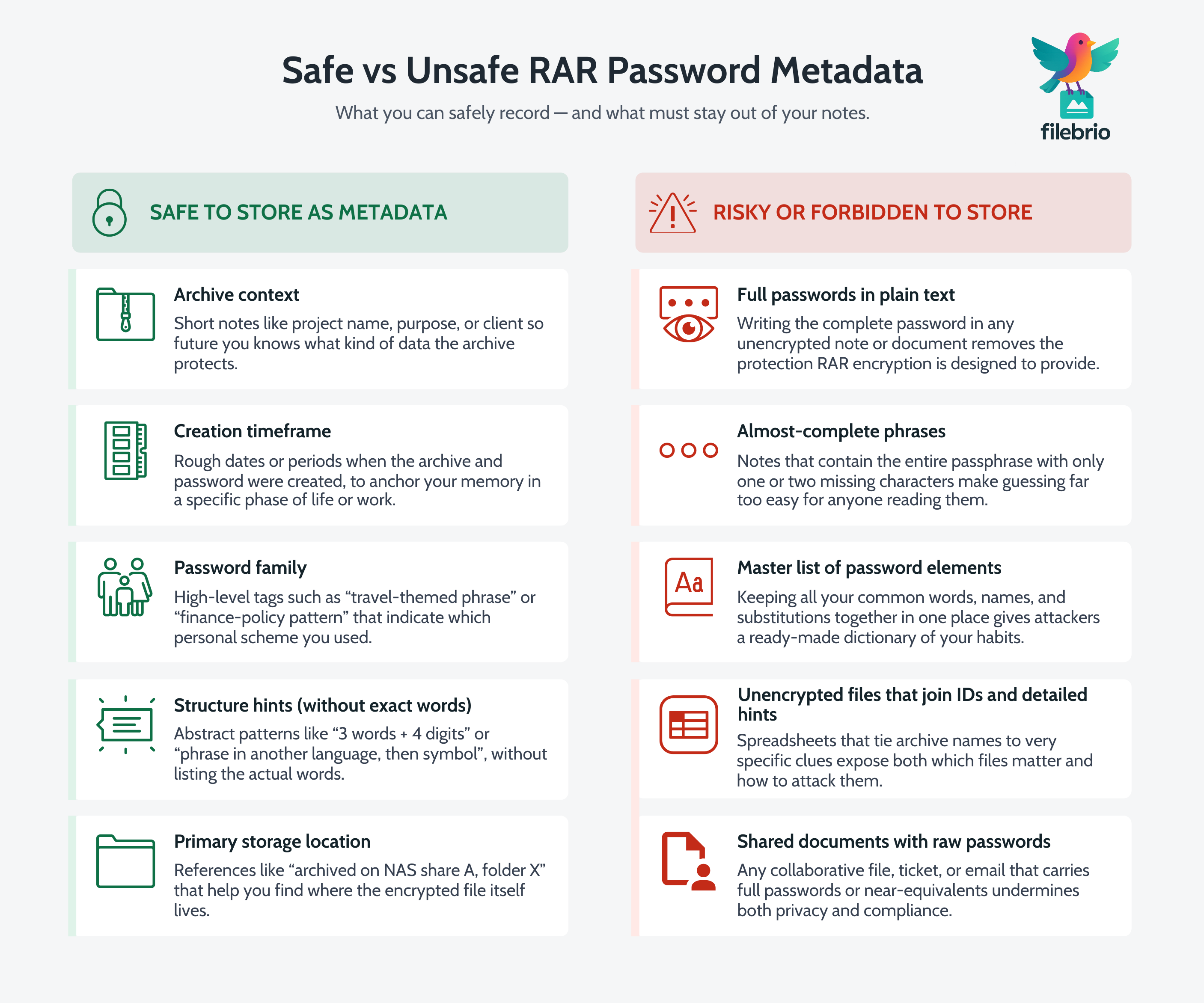
🗂️ What Counts as RAR Password Metadata (And What Never to Store)
“Metadata” can sound abstract, so it helps to be very concrete about what belongs in your notes and what should never appear there. The goal is to store enough information to jog your memory and guide future diagnostics, without writing down the full secret in a way that would help an attacker.
Typical safe password metadata for a RAR archive might include:
- Archive context — project name, purpose, department, or client.
- Creation timeframe — roughly when the archive and password were created.
- Password “family” — which of your personal schemes or categories it belongs to (e.g., “long passphrase based on travel theme”).
- Structure notes — high-level hints like “3 words + 4 digits” or “phrase in another language,” without naming the actual words.
- Storage location — where the archive itself is primarily stored (disk, share, or system).
On the other hand, risky or forbidden metadata includes:
- Full passwords written in plain text.
- Near-complete phrases where only one character is missing.
- Lists of all your password elements in one place.
- Unencrypted files that combine archive identifiers with very specific password clues.
If you want a deeper breakdown of safe personal strategies, see guidance like how to organize metadata for your RAR passwords safely ↗️, which focuses on individual users and their long-term habits rather than corporate workflows.
Another critical point is retention over time. Metadata is only useful if it survives device failure and migration. That is where storage planning comes in — especially for users with many archives or complex environments where ways to retain long-term memory of your RAR passwords ↗️ become a practical, everyday concern rather than a theoretical one.
💼 All-In-One Hub for RAR Password Knowledge
As your number of encrypted archives grows, scattered notes quickly become a liability. Some hints are on paper, others in email drafts, some in text files on old laptops. When you finally need one specific password pattern years later, you end up spending more time searching your own notes than working with the archive.
What you actually need is an organized hub for RAR-related knowledge: one place where archive diagnostics, password metadata, and long-term access planning come together — always under your control, always offline.
FileBrio RAR Master helps here by acting as a central point for understanding your archive landscape, while your password metadata lives in the secure storage method you choose (for example, an encrypted vault or dedicated password manager). Instead of guessing blindly, you can:
| Your Pain Point | Why It Hurts | How a Structured Hub Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Dozens of archives, unclear passwords. | Difficult to know which password family belongs to which file. | Use archive diagnostics plus metadata notes to cluster and label them. |
| Old archives on unknown devices. | Risk of losing track of both files and their hints. | Catalog locations and associate metadata with each archive. |
| Fear of forgetting a single critical password. | Strong encryption means no easy reset if memory fails. | Document patterns and context in a safe, structured way. |
To understand what the application itself offers, you can review the dedicated overview of FileBrio RAR Master features ↗️, which describes its capabilities for archive analysis, repair diagnostics, and responsible password-handling modes — all designed for privacy-first, on-device use.
For many users, the best strategy is a combination: use FileBrio RAR Master to inspect and understand your archives, and pair it with documented personal practices for how to reinforce protection of your encrypted RAR files ↗️, including structured, well-protected metadata.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
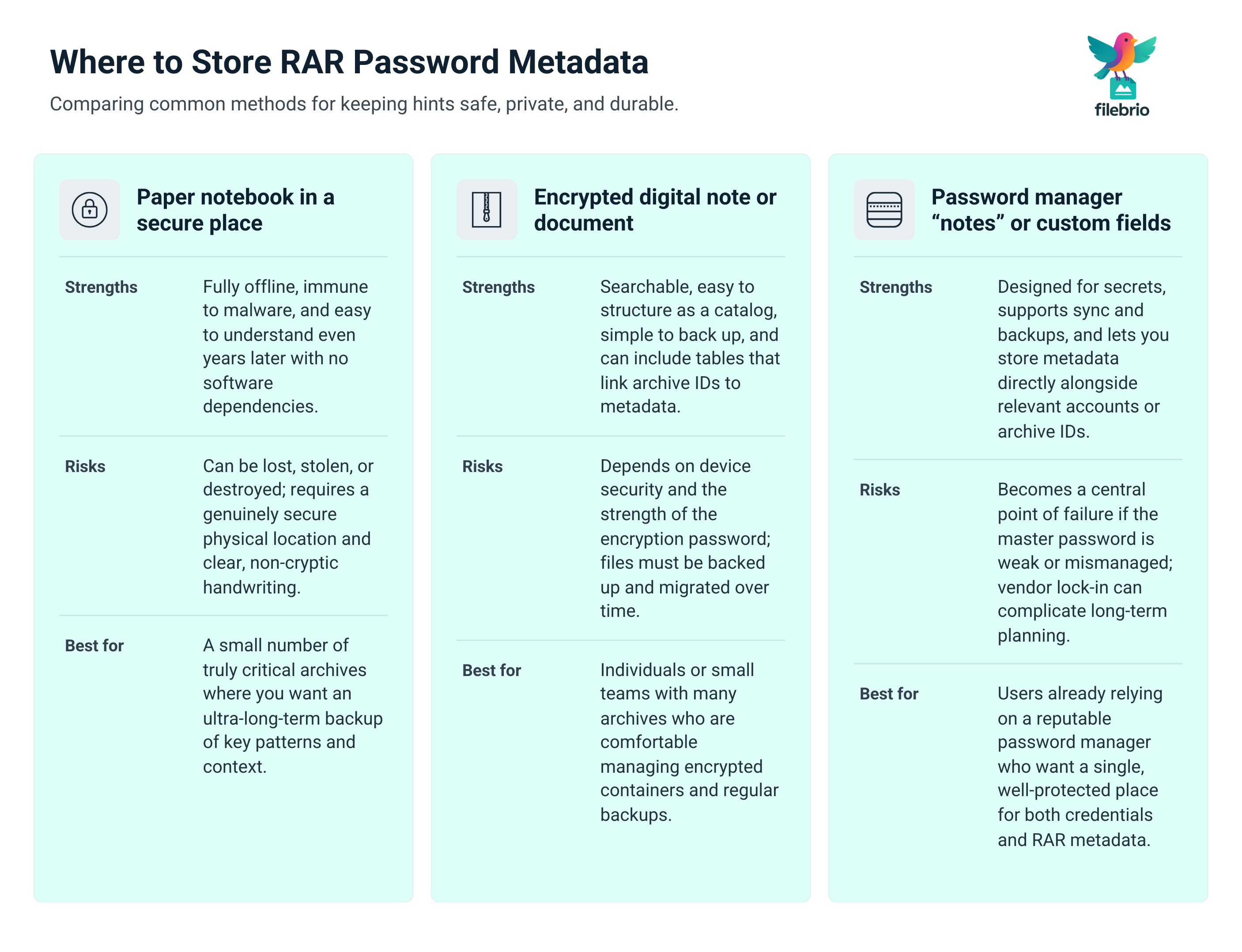
📁 Storage Options: From Paper Notes to Password Managers
Once you know what to store, the next step is deciding where and how. There is no single perfect option, but some combinations are clearly safer than others.
Common approaches for storing RAR password metadata include:
- Encrypted password managers — ideal for storing structured hints linked to specific entries or archive IDs.
- Encrypted note files or containers — such as secure documents where you maintain a catalog of archives and their metadata.
- Physical notebooks in secure locations — useful as an offline backup for key patterns and context, if treated like any other sensitive asset.
Whatever you choose, redundancy is critical. Devices fail, disks die, and cloud access can be revoked. Practical guides on ways to prevent losing your RAR data on storage devices ↗️ highlight the importance of thoughtful backup strategies for the archives themselves; your metadata needs the same care.
If you handle very large collections, long-term stability matters as well. You do not want a situation where the archives are carefully preserved but the system that stored your hints has vanished or become incompatible. Patterns from how to manage large RAR files without risking data ↗️ apply here too: choose solutions that are durable, portable, and well-documented enough that you (or your successors) can still use them in ten years.
In practice, a hybrid setup works best: keep primary metadata in an encrypted manager or vault, backed by occasional printed summaries stored securely, plus clearly documented procedures for future migration if tools or platforms change.
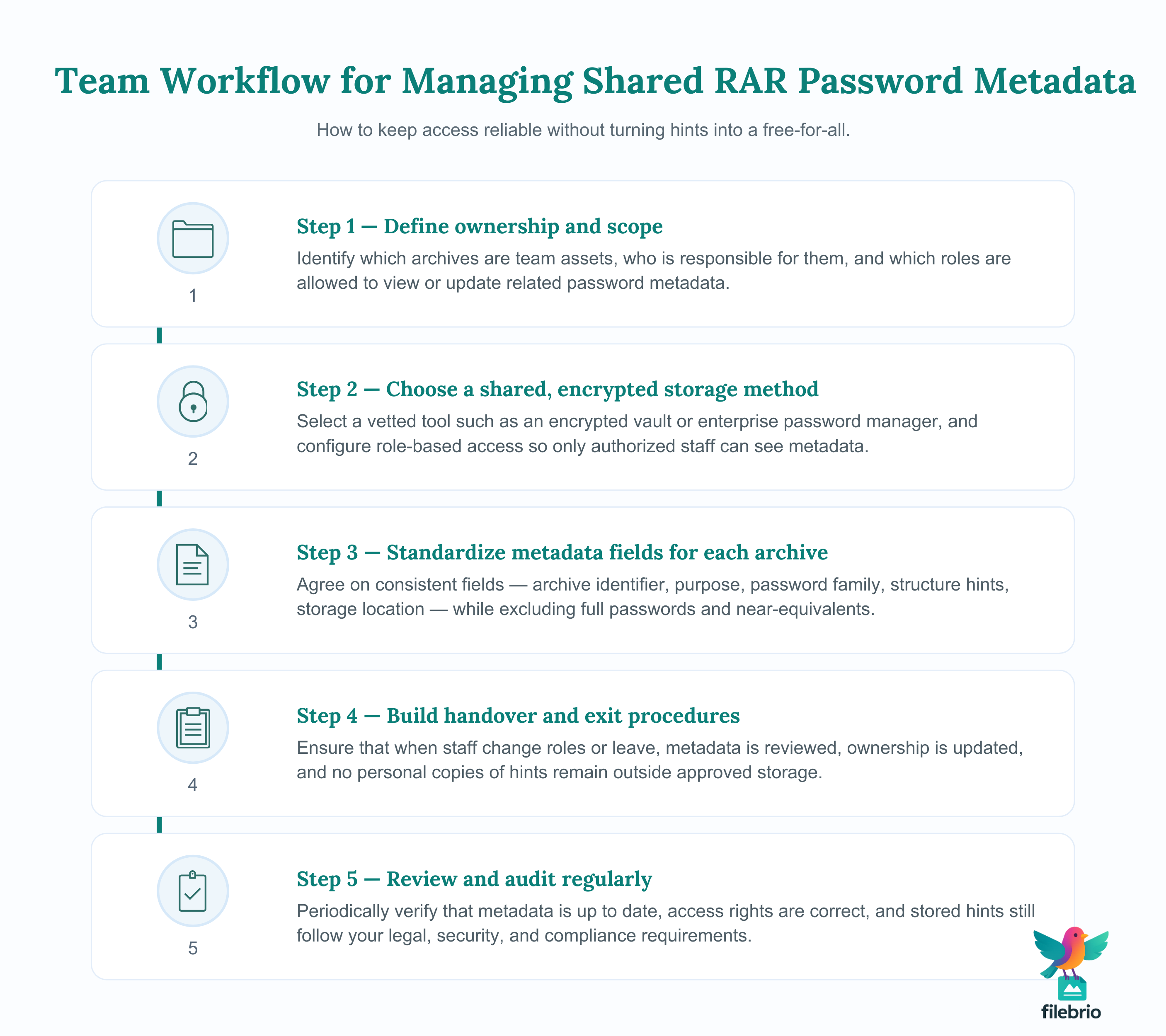
🌐 Sharing and Team Scenarios Without Losing Control
In organizations, RAR password metadata often needs to survive staff changes, role rotation, and audits. A single employee’s personal notes are not enough; you need a documented, shared approach that preserves both access and accountability.
Guides like how teams can organize shared RAR password metadata ↗️ emphasize the importance of distinguishing between individual knowledge and team assets. The key is to design a system where authorized personnel can retrieve the right information without creating a free-for-all of sensitive hints.
Some practical recommendations include:
- Role-based access to encrypted vaults where metadata is stored.
- Clear ownership records documenting who is responsible for each archive or project.
- Handover procedures when staff leave, ensuring metadata is updated and remains accessible to successors.
Long-term continuity is particularly important for organizations with regulatory or archival obligations. Strategies from how teams can preserve long-term access to encrypted RAR files ↗️ are directly relevant here, especially when archives must remain accessible for many years or decades under strict compliance requirements.
In such environments, the metadata itself becomes part of your governance framework. It supports audits, internal reviews, and disaster recovery plans — but only if it is stored securely, updated consistently, and tied to clear policies about legitimate use.
🔒 Secure Offline Solution for Metadata and Archives Together
Eventually, all of this planning converges on a simple question: when you need to regain access to an old encrypted archive, how do you combine metadata and tools in a way that is both safe and effective?
A privacy-first approach keeps both the archives and their supporting metadata under your direct control. You avoid uploading sensitive files to unknown websites, and you rely on trusted, offline tools to analyze their structure, confirm their health, and estimate whether your documented password patterns are realistically recoverable.
FileBrio RAR Master fits into this workflow as the on-device engine that understands your archives technically, while your protected notes describe the human story behind each password. Together, they allow you to:
- Inspect archives safely without exposing them to third-party servers.
- Validate your documentation against real headers, encryption modes, and format versions.
- Estimate realistic effort with tools such as the dedicated time-to-crack calculator ↗️ when contemplating limited, lawful password attempts.
For cases where access decisions intersect with policy or legal questions, you can consult the official legal and responsible use policy ↗️, which clarifies how the software is intended to be used and which scenarios require special care.
When you are ready to formalize this workflow on your own systems, you can obtain the toolkit from the official FileBrio download page ↗️, then pair it with carefully designed metadata practices and long-term planning resources such as how to preserve access to your decade-old RAR files ↗️. The result is a sustainable, offline model where your encrypted archives stay private — and future you still has a realistic path to them.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
⚖️ Legal Reminder
All of the practices described in this article assume that you are working exclusively with archives you own or are clearly authorized to manage. Secure password metadata and powerful offline tools are meant to protect long-term access to your data, not to bypass protections on someone else’s files.
In business contexts, you should align your metadata storage, password policies, and archive handling workflows with internal governance and external regulations. That includes documenting who has access to what, how access is audited, and how sensitive information is removed or revoked when roles change. For additional clarity about acceptable use, licensing, and support channels, refer to the official RAR Master help and answers ↗️ and the linked legal resources.
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📚 See Also
- How Naming Conventions And Everyday Habits Reveal Useful Clues About Your Archive Security ↗️
- How To Create Strong Yet Memorable RAR Passwords That You Won’t Lose In The Future ↗️
- Common Mistakes When Working With Password-Protected RAR Archives ↗️
- Why Offline Recovery Tools Are Safer For Privacy ↗️