
RAR/WinRAR File Passwords Explained: How Encrypted Archives Work and What Access Options You Have
You double-click a RAR or WinRAR archive and instead of familiar files, you see a password prompt or a confusing error. Somewhere in the back of your mind you remember “encryption” and “security,” but it is not clear what your options really are. Can you reset the password? Is there a way to “open without password”? Are online “unlockers” actually doing anything special—or are they just asking you to upload sensitive data and hope for the best?
Most of this confusion comes from not having a clear mental model of what a RAR password does. A RAR/WinRAR password is not just a door code—it is part of a cryptographic system that decides, with mathematical precision, who can see what. Once you understand how passwords, keys, headers, and formats fit together, it becomes much easier to tell which access paths are realistic, which are wishful thinking, and how to work safely with archives you legitimately own.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📝 TL;DR — What a RAR Password Really Does
A RAR/WinRAR “password” is not just a lock screen—it is part of a cryptographic system that decides whether your data can be decrypted at all. When you protect an archive, the software turns your password into a cryptographic key and uses modern encryption algorithms to transform your files into unreadable data. To access the contents later, the software must rebuild the exact same key from the exact same password. If the password is wrong or truly lost, there is no built-in reset button or master override.
This has three important consequences. First, access depends entirely on the password you chose: its length, structure, and how well you remember it. Weak or predictable choices may allow limited recovery if you still have clues about your habits, while long random strings can make an archive practically unrecoverable once forgotten. Second, not all “password problems” are actually password problems—corruption, missing volumes, or encrypted headers can also block access, even with the right password. Finally, safe handling is about more than just guessing: you should diagnose the archive’s condition, evaluate whether recovery is technically realistic, and keep everything offline and under your control when archives contain sensitive data you legitimately own.
Once you see passwords as part of a larger encryption model, it becomes easier to answer practical questions: when it is worth trying to recover a password, when the archive is mathematically out of reach, why online “unlockers” rarely deliver on their promises, and how to create policies and habits that keep future passwords strong and manageable instead of turning your own security into a permanent lockout.
🧠 RAR Passwords and Encryption: The Big Picture
At a high level, a RAR password is a human-friendly way to control a machine-level secret: the encryption key. When you create an encrypted archive, WinRAR does not store your password inside the file. Instead, it feeds your password into a mathematical function that produces a cryptographic key. That key is what ultimately protects the data.
The key idea is that the same password always produces the same key. When you enter your password later, the software repeats the process and checks whether the derived key can successfully decrypt the encrypted data. If yes, the content becomes readable. If not, the archive remains opaque. For a broader, format-level view of how this works in RAR4 and RAR5, see how RAR4 and RAR5 secure your protected data ↗️, which explains how ciphers, modes, and headers combine to protect your files.
From this perspective, your password is less like a simple door code and more like a recipe that generates the exact key needed to reverse the encryption. This is why small changes matter so much: “Password1!” and “Password1?” may feel similar to you, but to the key derivation function they are entirely different ingredients that produce unrelated keys.
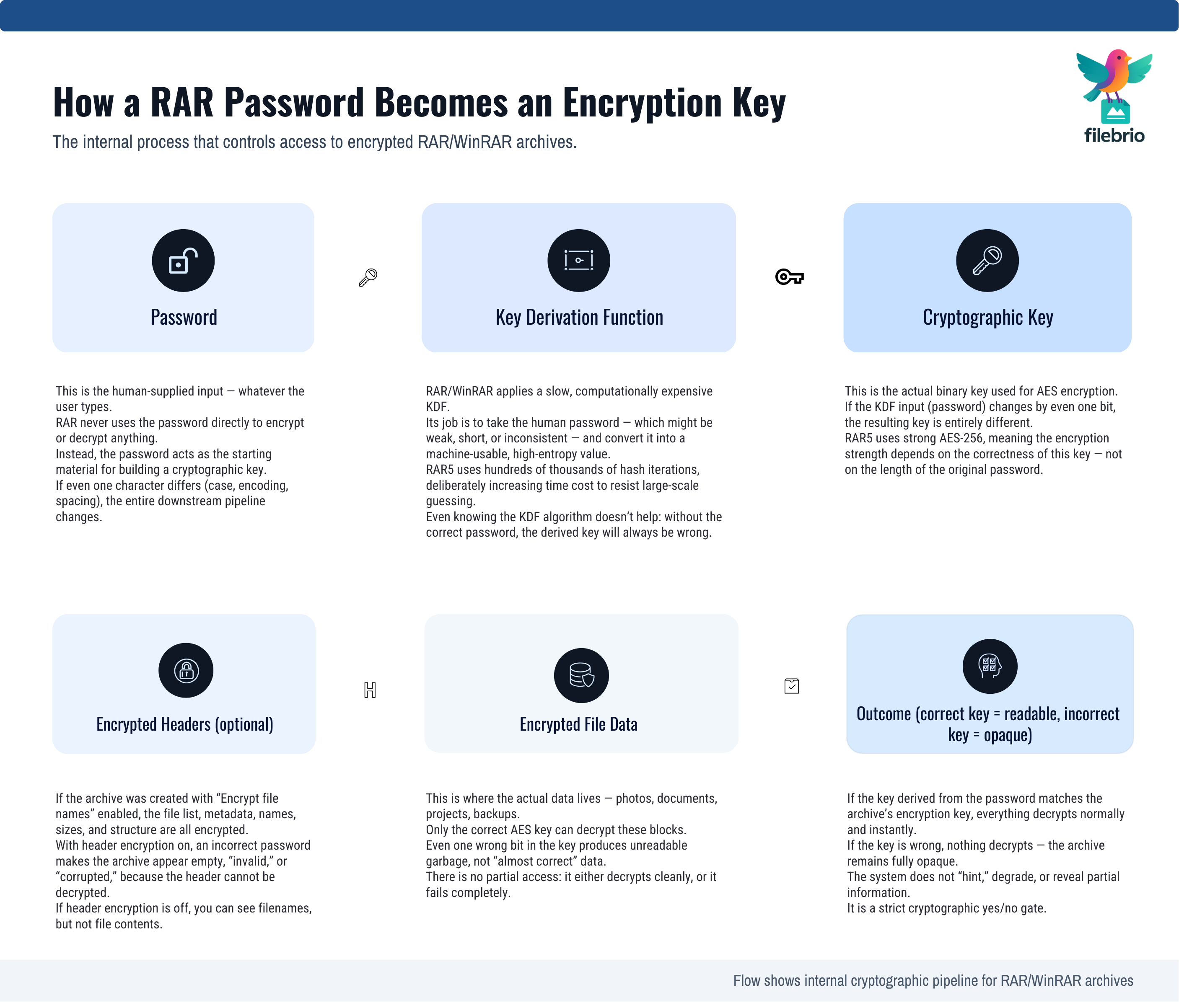
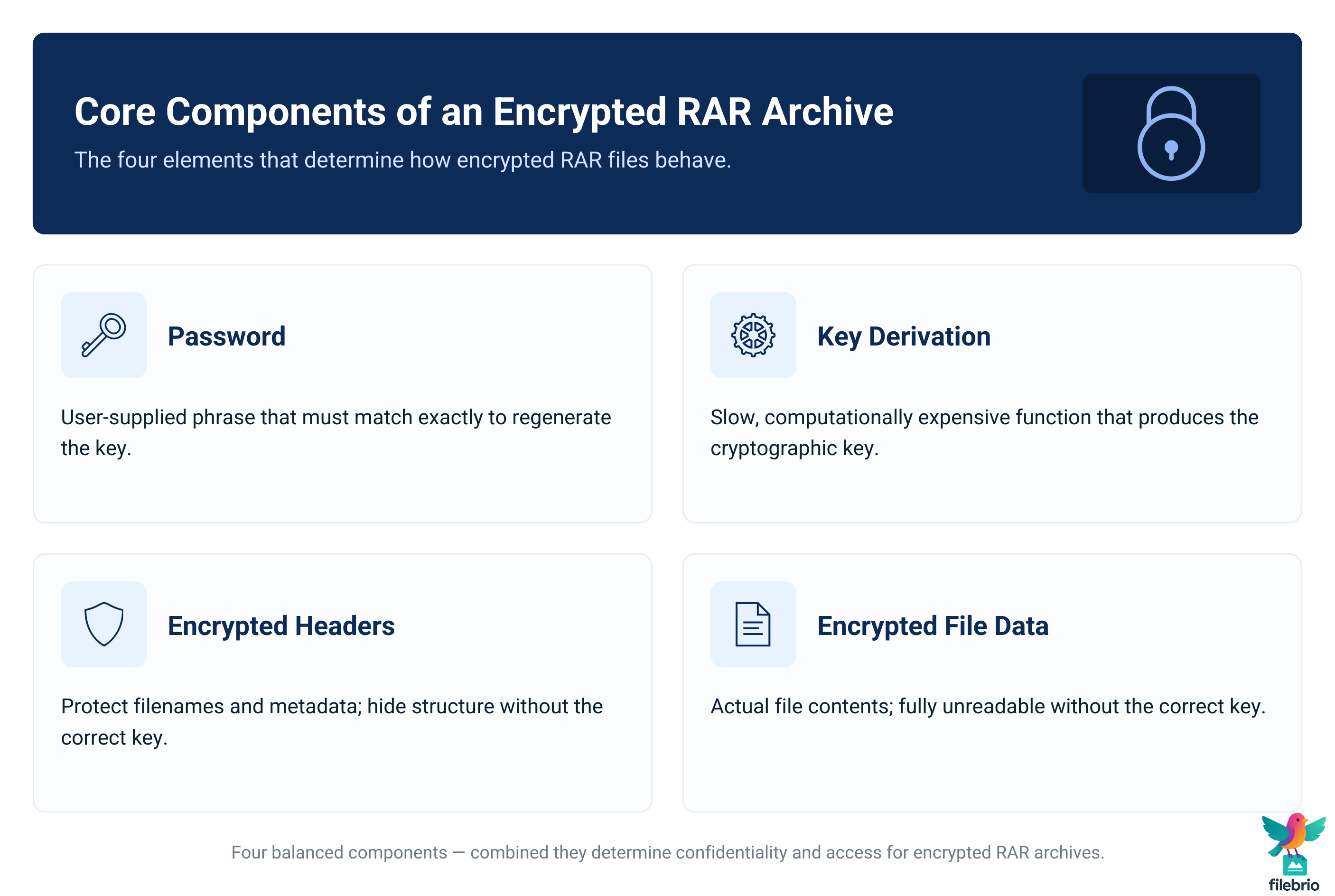
🔐 Core Components: Password, Key, Headers, and Data
To understand your real access options, it helps to break the system into components. A typical encrypted RAR archive involves four main pieces:
- Password: the phrase or string you choose and must later remember.
- Key derivation: the function that turns your password into a strong cryptographic key.
- Encrypted headers: optional protection for filenames and metadata.
- Encrypted file data: the actual contents of the files stored in the archive.
Key derivation is deliberately designed to be computationally expensive. RAR5, for example, significantly increases the work required to turn a password into a key compared to older schemes. This raises the cost of each attempted password. A deeper look at this design is available in how the RAR5 KDF strengthens your encrypted RAR file ↗️, which explains why modern key derivation functions are crucial to long-term security.
On top of this, the archive may encrypt not only the file data but also metadata such as filenames and folder structures. When headers are encrypted, you may not see any list of files until the correct password is supplied. This tight coupling between password, key, headers, and data is what gives RAR archives both their security and their sometimes unforgiving behavior when a password is mis-remembered.
🧮 RAR4 vs RAR5: Same Idea, Stronger Protections
RAR4 and RAR5 share the same basic philosophy—use a password to derive a key, then encrypt the data—but differ in how aggressively they apply that philosophy. RAR5 is designed to be more secure and modern than RAR4, especially in how it handles key derivation, metadata, and internal structures.
From a user’s perspective, the key differences often show up as:
- Stronger key derivation in RAR5: each password attempt takes more time, which dramatically reduces the rate at which someone can test guesses.
- More flexible encryption options: you may be able to encrypt headers and additional metadata in ways that were less common or less robust in older archives.
- Improved integrity checks: better detection of corruption or tampering, which can prevent partially damaged data from being silently treated as valid.
These improvements are good for protecting your data, but they also mean that an archive created with a strong RAR5 password can become effectively unrecoverable once that password is genuinely lost. For a discussion of why some archives cross a line where no realistic recovery remains, see why some RAR archives become impossible to open ↗️, which explains how cryptographic strength and archive structure can combine to close off practical access paths.
⏱️ How Password Strength Shapes Your Real Access Paths
When people talk about “strong” passwords, they usually think about resisting attackers. But the same strength also affects your ability to recover access later if something goes wrong. The core concept behind this is entropy—a measure of how many possibilities a password represents.
A short password drawn from a small character set has relatively low entropy. If you still remember rough patterns or have good clues about your habits, it may be feasible to check a constrained set of possibilities for an archive you legitimately own. However, as password length grows and character sets broaden, the number of possible combinations explodes. The article on how length impacts protection of your RAR password ↗️ shows how adding just a few characters can multiply the work by orders of magnitude.
Even with powerful hardware, this quickly hits real-world limits. Conceptual timing models—like those described in how to understand password guessing time estimates ↗️—demonstrate that beyond a certain entropy level, attempting to test every candidate password becomes impractical on any reasonable timescale. This is exactly why strong passwords are recommended and why, once lost, some archives remain out of reach even to their legitimate owners.
💼 All-In-One Toolkit for Understanding and Managing RAR Passwords
Once you see how tightly passwords and encryption are connected, it becomes clear that “working with RAR passwords” is really about managing the entire lifecycle of encrypted archives: creation, diagnostics, feasibility analysis, and—only when justified—carefully bounded recovery work on files you legitimately own. Juggling this with ad-hoc tools is difficult, especially if you are responsible for multiple archives or a whole team.
A dedicated desktop suite can help by centralizing the key tasks you actually need:
- Format-aware diagnostics that distinguish RAR4 from RAR5 and highlight encryption options used when the archive was created.
- Non-destructive integrity checks to show whether corruption or missing volumes play a role before you even touch passwords.
- Guided feasibility evaluation, where entropy, structure, and context are combined to decide whether any recovery attempt makes sense.
- Offline, privacy-first operation, so your encrypted archives never leave your own environment.
If you want to see how such capabilities can be packaged in practice, the all-in-one RAR recovery toolkit ↗️ overview illustrates how diagnostics, recovery features, and policy-friendly controls can live in a single application instead of scattered tools and risky web pages.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
🔍 Diagnosing Why a Password-Protected Archive Won’t Open
Before you think about “recovering” or “resetting” any password, you should answer a simpler question: why isn’t the archive opening right now? Not all failures are caused by bad passwords. Some are about damaged data, format mismatches, or unexpected encryption settings.
A methodical diagnostic approach usually includes:
- Reading error messages carefully: “wrong password” looks very different from “unexpected end of archive” or checksum errors.
- Checking the archive structure on a copy: ensuring that files are not truncated, that all volumes of a multi-part set are present, and that storage devices are healthy.
- Reviewing metadata: internal flags and headers often reveal whether encryption is enabled, whether recovery records exist, and which format version is used.
A good starting point is to follow the high-level steps described in how to safely diagnose your locked RAR file ↗️, which focuses on minimizing risk while you determine whether you are facing a password issue, a structural problem, or a combination of both. Many users discover that what looked like a “forgotten password” is actually corruption or incomplete download—situations that need repair, not password work.

🧱 How Encrypted Headers Change What You Can See
One of the most confusing aspects of RAR passwords is how they interact with headers. In some archives, you see a file list immediately but get errors when you try to extract. In others, the archive appears almost empty until you enter a password. The difference often comes down to whether header encryption is enabled.
When headers are encrypted, the filenames and directory structure are protected alongside the file data itself. From an outside perspective, there is almost nothing to inspect without the correct key: no meaningful names, no obvious structure, and limited metadata. This behavior is explained in detail in how encrypted headers hide your protected RAR contents ↗️, which shows why content discovery becomes essentially impossible without the right password.
For access planning, this means you can no longer rely on filenames as clues. If you do not remember the password, you must base feasibility decisions on other signals such as archive size, context, and any notes you kept about your own password patterns. Header encryption strengthens confidentiality, but it also makes “partial insight” approaches impossible—the archive either decrypts fully with the correct password, or stays opaque.
🌐 Offline vs Online Handling: Where Your Password Really “Lives”
Another common source of confusion is where your password actually exists. With web accounts, you can often click “forgot password” and rely on a provider to manage resets. With encrypted RAR archives, there is no such centralized authority—everything lives inside the archive and the software that created it.
This has implications for how you choose tools and workflows. Offline tools that process your archives locally respect the original security model: they work directly with the encrypted data on your machine, never sending it to third-party servers. In contrast, online “unlockers” typically require you to upload the entire archive, surrendering control and visibility over how it is handled.
From a risk perspective, it is almost always safer to keep both your archives and any password-related work inside your own environment. A high-level comparison of these approaches is available in offline vs online RAR recovery ↗️, and privacy aspects are explored in why offline tools keep your encrypted RAR data private ↗️. Together, these perspectives reinforce a simple rule: passwords and sensitive archives belong on systems you control, not in unknown cloud services.
🛡️ Secure Offline Suite for Realistic, Privacy-First Access Options
Once you decide to handle RAR passwords only on archives you own and only in environments you trust, the next step is choosing tools that reflect those priorities. A secure offline suite can provide:
- Integrated password and structure analysis so you can see at a glance whether an archive is even a candidate for recovery work.
- Carefully constrained recovery features that respect legal boundaries and focus on realistic search spaces based on your own password habits.
- Support for long-running tasks when justified—without sending your data off to external servers.
- Documentation and guidance aimed at helping you understand what is and is not possible before you invest significant effort.
On the recovery side, an example of such functionality is a RAR password recovery tool ↗️ that operates entirely on your local machine, working only with archives you legitimately own. To avoid overestimating what any tool can do, it is useful to pair this with conceptual calculators such as the estimate RAR password recovery time ↗️ feature, which connects password design choices with realistic timeframes instead of marketing promises.
Finally, because password work sits close to legal and ethical lines, organizations often rely on documented frameworks. Software backed by a clear legal and responsible use policy ↗️ makes it easier to align actual usage with compliance rules and to demonstrate that your access to encrypted archives stays within defined limits.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
🧾 Turning Password Rules Into Practical Access Policies
Understanding RAR passwords at a technical level is only half the story. In teams and organizations, you need policies that translate cryptographic facts into predictable behavior: how passwords are chosen, who can change them, how access is documented, and what happens when someone leaves the company.
Good RAR password policies usually address questions like:
- What minimum length and complexity should archive passwords have?
- Who is allowed to create encrypted archives, and for what kinds of data?
- How are passwords or metadata recorded so that legitimate future access remains possible?
- What is the approved process if a team loses access to an important archive?
Designing these rules is not just a technical exercise; it also involves compliance and risk management. A practical starting point is outlined in how to design secure password rules for your business RAR files ↗️, which connects password quality, organizational roles, and long-term accessibility. Once policies are in place, they make it easier to justify why certain archives are recoverable, why others are not, and how you will respond to future access issues without improvisation.
🔄 Future-Proofing Your Archives So Access Stays Possible
The best time to think about RAR passwords is when you create the archive, not years later when you discover you can no longer open it. Future-proofing is about choosing password strategies, metadata practices, and archive formats that keep access possible without sacrificing security.
Key practices include:
- Choosing structured, high-entropy passwords that are long and robust but still anchored in patterns you can document safely.
- Storing password metadata securely—not the password itself, but descriptions and context that help future you (or authorized colleagues) understand how to approach access. Ideas for doing this responsibly are discussed in how to preserve password metadata for your encrypted RAR files ↗️.
- Balancing security and access over time, especially for archives with long retention periods. Guidance on how to strengthen protection without locking yourself out is given in how to reinforce protection of your encrypted RAR files ↗️.
- Planning recovery paths in advance, so that if an archive becomes inaccessible, you already know which steps to follow and who is responsible.
When future-proofing is treated as part of regular data hygiene—rather than an afterthought—it drastically reduces the number of situations where you need to contemplate password recovery at all. Instead, your archives remain both secure and practically usable throughout their lifespan.
⚖️ Legal & Ethical Context for RAR Passwords
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📚 See Also: Further Reading on RAR Security and Access
- How RAR Security Works and Why Passwords Can’t Be Reset Like Email Credentials ↗️
- How to Evaluate Safe Options for Regaining Access to a RAR/WinRAR Archive You Own ↗️
- Open RAR Files Without a Password? What’s Possible, What Isn’t, and How to Access Your Data Safely ↗️
- Why Offline Recovery Tools Are Safer for Privacy ↗️
- Common Mistakes When Working With Password-Protected RAR Archives ↗️
- Why Some RAR Archives Become Impossible to Open — Security Explained ↗️
- Opening RAR/WinRAR Archives With or Without a Password: A Practical Guide to Safe Access Options ↗️