
RAR Encryption Explained: How RAR4 and RAR5 Protect Your Data
You see a small RAR icon, type a password, and either the archive opens or it doesn’t. Behind that simple moment sits a full encryption system: key derivation, ciphers, headers, and integrity checks. The differences between older RAR4 and newer RAR5 formats directly affect how safely your data is protected, and what happens if you later forget your password.
This article walks through RAR encryption at a high level, explains how RAR4 and RAR5 protect confidentiality, and clarifies why some archives are realistically recoverable while others are mathematically out of reach. The focus is strictly on your own archives, lawful usage, and safe, privacy-first diagnostics.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
⚡ TL;DR — How RAR Encryption Protects Your Data
RAR encryption uses strong cryptography to transform your files into unreadable data that can only be decrypted with the correct password-derived key. RAR4 already provides solid protection; RAR5 strengthens this even further with a more robust key derivation function and improved security features.
Key ideas:
- RAR does not “store” your password; it derives encryption keys from it using a key derivation function (KDF).
- RAR5 significantly increases the cost of guessing each password candidate compared to RAR4.
- Encrypted headers and filename encryption can completely hide file names and structure.
- Strong encryption means there is no reset button — if you lose the password, access may be mathematically impossible.
The rest of this article breaks down these points, helping you understand what you can reasonably expect from RAR encryption and where the hard limits are.
🧠 RAR Encryption Basics: What “Protected Archive” Really Means
When you create a password-protected RAR or WinRAR archive, you are not just “locking a file with a code.” Under the hood, the archive is split into blocks of data, and those blocks are transformed using a modern cipher (like AES) and keys derived from your password.
At a high level, RAR encryption provides:
- Confidentiality: outsiders cannot read the original file contents without the correct password.
- Controlled visibility: depending on settings, even filenames and headers may be hidden.
- Integrity checks: mechanisms to detect whether data has been altered or corrupted.
This is why RAR behaves very differently from a web account: there is no server that can reset your password. The logic behind this is explained in more detail in resources such as how RAR security works and why passwords can’t be reset like email credentials ↗️, which emphasize that the archive itself has no “backdoor” or central recovery authority.
🧱 RAR4 vs RAR5: Structural and Security Differences
RAR4 and RAR5 share the same goal — protecting your data — but they differ in how they derive keys, structure headers, and support additional features. From a security point of view, three aspects matter most:
- Key derivation function (KDF): RAR5 uses a more demanding KDF, which significantly increases effort required to test each password candidate.
- Metadata and headers: RAR5 offers more flexible header structures and options for encrypting metadata, including file names.
- Repair and usability features: RAR5 improves how recovery records and quick-open data are stored, affecting both resilience and user experience.
Understanding which format your archive uses is an important first step when assessing risk, recovery feasibility, and long-term protection strategies. Those bigger-picture considerations tie closely into how to strengthen RAR archive security while preserving future access ↗️.
🔐 Inside the Encryption Flow: Keys, KDFs, and Password Strength
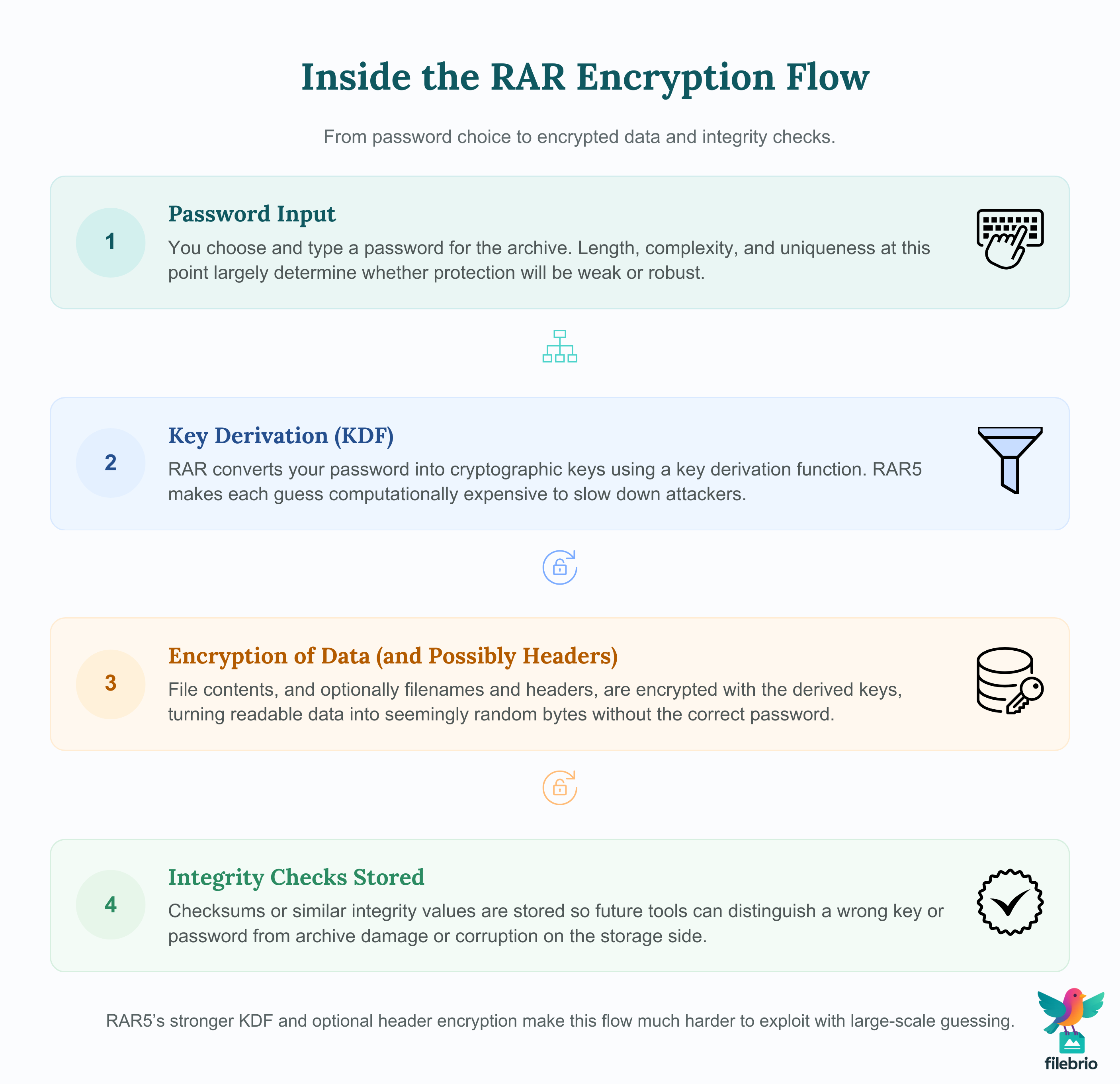
At a conceptual level, a RAR encryption flow involves several stages. While the exact implementation details are technical, you can think of the process like this:
| Stage | What Happens | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Password input | You choose and type a password for the archive. | Human choice: length, complexity, and uniqueness start here. |
| 2. Key derivation | RAR uses a KDF to convert your password into cryptographic keys. | RAR5’s stronger KDF raises the cost of trying each password candidate. |
| 3. Encryption | File data (and optionally headers) is encrypted using the derived keys. | Without the right key, data appears as random bytes. |
| 4. Integrity checks | Checksums or similar values are stored to detect later corruption. | Helps distinguish “wrong key” from “damaged archive.” |
RAR5’s KDF design is especially important. By making each password candidate computationally expensive to test, it protects against large-scale guessing attempts, especially when combined with strong passwords. A high-level discussion of why this matters is covered in why the RAR5 key derivation function matters for security ↗️, which focuses on concepts rather than specific attack techniques.
Of course, encryption is only as strong as the password behind it. The relationship between password length, randomness (entropy), and practical guess difficulty is explored in how password length and entropy affect guessing complexity ↗️. For RAR users, the takeaway is simple: strong cryptography plus weak password still equals weak protection.
💼 All-In-One Solution for Understanding Your Own Encrypted RAR Archives
As you accumulate more RAR archives over time, it becomes harder to keep track of which format each archive uses, how strong the corresponding passwords are, and whether certain old archives are still realistically accessible. Typical pain points include:
- Having a mix of RAR4 and RAR5 archives without clear documentation.
- Not knowing if an archive’s issues are due to encryption strength or file damage.
- Uncertainty about whether a forgotten password is still feasible to recover.
- Relying on scattered tools or risky online services for diagnostics.
FileBrio Office Suite, and particularly FileBrio RAR Master, is designed to centralize these tasks in a single, offline environment that respects your privacy and your data boundaries. Instead of juggling multiple utilities, you can use one toolkit to:
| Your Need | How FileBrio RAR Master Helps |
|---|---|
| Identify RAR4 vs RAR5 archives | Format-aware diagnostics highlight which security model applies to each archive. |
| Check archive health | Header and metadata analysis helps distinguish password issues from corruption. |
| Understand realistic recovery chances | Conceptual feasibility checks align your expectations with cryptographic limits. |
| Keep everything private | 100% local processing means no RAR files or metadata are uploaded anywhere. |
This integrated perspective is summarized in the FileBrio RAR Master features ↗️ overview, which shows how diagnostics, lawful recovery workflows, and archive health checks fit into one consistent toolset.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
🧬 Encrypted Headers, Filenames, and What Metadata Still Shows
RAR does more than encrypt file contents. Depending on your settings, it can also encrypt headers and filenames, restricting what is visible before the correct password is entered. This is particularly important in shared or cloud environments, where even file names can reveal sensitive information.
Conceptually, there are different visibility levels:
- Data-only encryption: file contents are encrypted, but filenames may remain visible.
- Filename encryption: file names are hidden until the correct password is provided.
- Encrypted headers: certain structural details about the archive are also concealed.
| Protection Level | What Outsiders See | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Contents encrypted, filenames visible | File list and structure, but no readable contents. | Convenient when filenames are non-sensitive. |
| Filenames encrypted | No meaningful file list until password is entered. | When file names themselves may leak private information. |
| Headers heavily protected | Minimal metadata; much of the structure is obscured. | High-privacy scenarios where even structural hints are sensitive. |
The implications of these modes are explored in articles like why encrypted headers make content discovery impossible ↗️ and RAR filename encryption explained: privacy, security, and diagnostic limits ↗️. Together, they show that stronger protection often means fewer diagnostic clues, which is a deliberate trade-off in favor of confidentiality.
📊 Table: Comparing RAR4 and RAR5 Security Features
To make the differences between RAR4 and RAR5 more concrete, it helps to see them side by side. The table below is simplified but highlights the most important aspects for everyday users who work with their own archives.
| Aspect | RAR4 | RAR5 | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key derivation strength | Older design, lower per-guess cost. | Stronger KDF with higher per-guess cost. | RAR5 offers better resistance to large-scale guessing. |
| Filename and header encryption options | Supported but more limited. | More flexible and robust protection of metadata. | RAR5 can hide more structural information when configured. |
| Recovery and quick-open features | Basic recovery records available. | Improved recovery blocks and quick-open records. | RAR5 improves usability and resilience against corruption. |
| Compatibility | Supported by many older tools. | Requires modern tools with RAR5 support. | Legacy systems may prefer RAR4; modern setups benefit from RAR5. |
From a planning perspective, it often makes sense to migrate important long-term archives to RAR5, especially when you combine that with good password practices and careful metadata handling. Guidance on how encryption choices affect long-term access is discussed in why RAR5 is more secure — and what that means for file access ↗️, which focuses on balance between stronger protection and practical usability.

🧪 How Encryption Affects Recovery Feasibility (Not Guaranteed Access)
Strong RAR encryption is a double-edged sword: it protects your data from unauthorized access, but it also means that forgetting the password can make recovery impractical or impossible. There is no master key or vendor “override” to open an encrypted archive without valid credentials.
When evaluating your own locked archive, consider three high-level factors:
- Format: RAR5 with a strong KDF is significantly harder to guess than older RAR4 with similar passwords.
- Password quality: length, randomness, and lack of predictable patterns increase difficulty dramatically.
- Technical constraints: available hardware and realistic time limits cap what is feasible.
High-level timing and complexity discussions, such as those in how to understand password guessing time estimates ↗️, help set expectations. At the same time, articles like why some RAR archives become impossible to open ↗️ explain that, beyond certain thresholds, no amount of effort can compensate for strong cryptography plus a truly unpredictable password.
From a safety standpoint, the important message is that strong encryption is working as intended when it limits options. Evaluating feasibility should happen in a controlled, offline environment with clear boundaries, not through untrusted online services that promise unrealistic results.
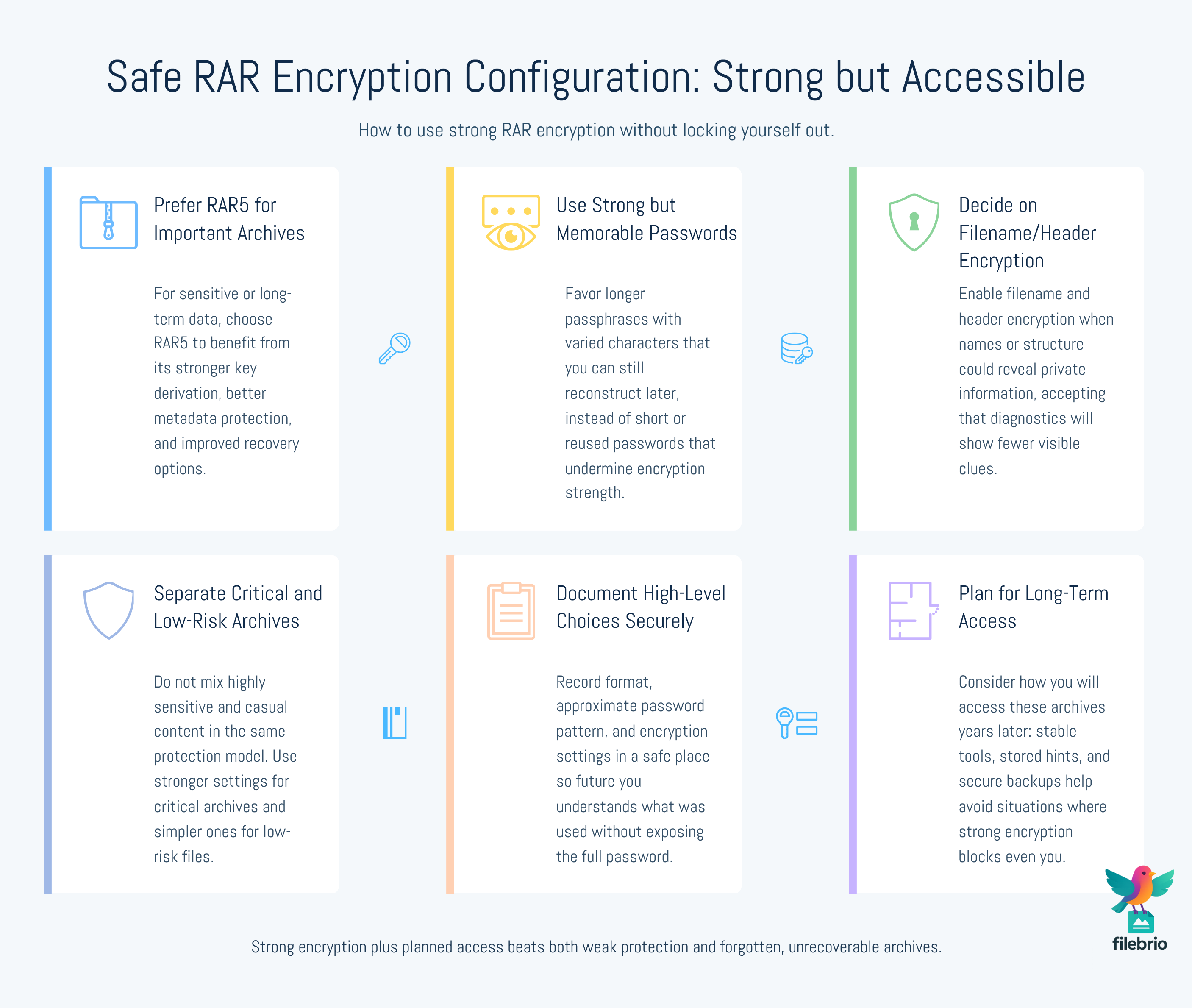
🛡️ How to Configure RAR Encryption Safely Without Locking Yourself Out
For everyday users, the challenge is to configure RAR encryption strong enough to protect sensitive data, while still allowing legitimate future access. That means thinking about both technical settings and human memory.
Some practical guidelines include:
- Prefer RAR5 for new, important archives: it provides a stronger KDF and better metadata protection.
- Use strong, memorable passwords: length and variability matter, but so does your ability to remember or reconstruct them later.
- Enable filename/header encryption when appropriate: especially when file names could reveal confidential information.
- Document your choices: keep safe, high-level notes about which pattern and format you used for critical archives.
| Goal | Configuration Choice | Supporting Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Protect confidential documents | RAR5, strong password, filename encryption enabled. | Store high-level password metadata in a secure, separate place. |
| Archive non-secret data with light protection | RAR4 or RAR5 with moderate password, filenames visible. | Note which archives are less sensitive; avoid mixing with critical ones. |
Designing passwords that are both strong and recallable is a separate skill, covered in how to create strong yet memorable RAR passwords that you won’t lose in the future ↗️. Aligning those habits with RAR5’s strengthened cryptography gives you a robust, long-term protection model.
🧲 Secure Offline Solution for Diagnostics, Estimates, and Lawful Recovery
One of the biggest risks with encrypted RAR archives is the temptation to upload them to online services that promise instant access or analysis. Even if the encryption is strong, sharing archives with unknown third parties exposes filenames (when not fully encrypted), sizes, and other contextual information that you may prefer to keep private.
Common frustrations that lead users toward online tools include:
- Uncertainty about whether an archive is damaged or simply protected by a strong password.
- No clear way to estimate how long a realistic password search might take.
- Lack of integrated tools that understand both RAR4 and RAR5 and their respective limitations.
- Confusion about legal boundaries when working with encrypted data.
FileBrio RAR Master is designed as a fully offline environment for exactly these scenarios. Within the FileBrio Office Suite, it provides:
| User Concern | FileBrio RAR Master Capability |
|---|---|
| “Is my archive structurally healthy?” | Diagnostics modules read headers and metadata to flag possible corruption. |
| “Is it worth trying to recover this password?” | High-level feasibility and time estimates consider format and complexity. |
| “How can I explore options safely?” | Offline recovery workflows focus on archives you legitimately own. |
| “Where do I learn about limits?” | Built-in guidance aligned with documented limitations and best practices. |
To see how offline, privacy-first workflows compare with riskier online unlockers, you can review the FileBrio RAR Master online vs offline comparison ↗️. For conceptual timing and feasibility analysis, the password estimation and time-to-crack calculator ↗️ offers high-level insights without exposing your archives anywhere.
When you decide to integrate these tools into your own setup, you can obtain them from the official FileBrio Office Suite download page ↗️, and if needed, review FileBrio pricing plans ↗️ to choose the edition that fits your use case.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
📁 When Strong Encryption Makes Recovery Unrealistic — By Design
It can be emotionally frustrating to discover that a forgotten password stands between you and important data. However, that frustration is also evidence that the encryption is doing its job. If it were easy for you to bypass your own password, it would likely be easy for others as well.
In practice, recovery becomes unrealistic when several factors converge:
- The archive uses a modern format such as RAR5 with a strong KDF.
- The password was long, diverse, and not based on simple patterns or dictionary words.
- You no longer remember enough context to meaningfully narrow down possibilities.
At that point, the relevant question is not “how do I get around the encryption,” but “how do I avoid repeating this situation in the future?” Articles like why some RAR archives become impossible to open ↗️ and RAR/WinRAR file passwords explained ↗️ are written to help you understand these limits and design better habits going forward.
If you are evaluating options for a currently locked archive that you own, it is wise to use structured, lawful decision-making frameworks such as those in how to evaluate safe options for regaining access to a RAR/WinRAR archive you own ↗️. These focus on realistic expectations and safe behaviors, not on circumventing cryptographic protection.
For questions about responsibilities, documentation, and compliance in more formal contexts, you can also consult the FileBrio RAR Master support & legal information ↗️, which outlines responsible-use guidelines, support boundaries, and other policy-related details.
⚖️ Legal and Ethical Reminder
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
🧩 See Also: RAR Encryption, Security, and Access Planning
- Why RAR5’s Stronger Security Matters for Real-World File Access ↗️
- What Known-Plaintext Concepts Reveal About RAR Encryption Models ↗️
- How to Tell Whether a RAR Archive Has Its Headers Encrypted ↗️
- How GPU Acceleration Influences RAR Password Guessing Difficulty ↗️
- Why Brute-Forcing RAR Passwords Has Practical and Legal Limits ↗️
- Why RAR Passwords Can’t Be “Reset” — and What Options You Actually Have ↗️
- What’s Possible (and Not Possible) When Opening a RAR File Without Its Password ↗️