
How to Prove Ownership of a RAR Archive in Corporate Environments
In business environments, encrypted RAR archives often become inaccessible due to staff turnover, poor documentation, incomplete handovers, or missing password metadata. Before any diagnostics or recovery work, an organization must clearly confirm who owns the archive and who is authorized to access it.
Compliance rules and internal audit requirements demand documented legitimacy before sensitive or regulated data can be opened. This article outlines how to verify ownership, establish a traceable authorization record, and prevent the documentation gaps that commonly lead to legal or security issues later.
🧭 Navigation
📌 TL;DR — Corporate Ownership Proof at a Glance
To establish ownership of an encrypted RAR archive in a business environment, you need:
- Documents showing the archive’s origin — project records, tickets, handover notes, or version-control logs.
- Role-based authorization — only designated owners, managers, or departmental custodians can grant access.
- Traceable chain-of-custody — who created it, who stored it, who accessed it, and how it moved between systems.
- Compliance alignment — proof must meet internal policies and any external regulatory requirements.
Without these, recovery attempts — even for legitimate business use — may violate internal rules or fail audit checks.

🏢 Introduction: Why Ownership Proof Matters in Business
In consumer contexts, establishing ownership of a locked RAR archive is often simple — the archive belongs to the device owner. But in enterprise environments, the situation is more complex. Archives may contain regulated data, customer information, intellectual property, or confidential materials tied to specific departments or projects.
Before any analysis or recovery begins, compliance and IT security teams need certainty that:
- the organization owns the content, and
- the requesting party is authorized to access or manage it.
Failing to document this can violate privacy laws, contractual obligations, or internal policy. This is why many organizations adopt structured diagnostic guidelines such as ways to tell what blocks your RAR file ↗️ — but none of those steps can begin without ownership clarity.
🧠 What “Ownership” Means in Corporate Terms
Corporate ownership does not simply mean “someone created the file.” Instead, it refers to:
- business ownership — the department, team, or legal entity responsible for the data;
- custodianship — individuals or roles tasked with managing or safeguarding the archive;
- authorization rights — who may approve access, decryption, or recovery attempts.
Even if an employee created the archive, the organization usually owns the contents. This affects how authorization is handled, who signs off, and how recovery efforts are documented.
🏢 A Safe, Audit-Aligned Way to Check Your Archive Before Any Recovery Steps
In corporate environments, the biggest risk isn’t the forgotten password — it’s taking action
before you know the archive’s true condition.
Countless teams lose time assuming the issue is “just a password,” when in reality the archive may have
encrypted headers, structural damage, or misaligned multi-volume segments that block access
regardless of authorization.
Before compliance teams approve anything, you need clarity that doesn’t expose sensitive data
or violate internal policy.
FileBrio RAR Master provides exactly that — a private, traceable first step that keeps the archive
fully offline and under organizational control.
- 🔐 Confirms encrypted-header behavior (no filenames visible is a security feature, not corruption)
- 📦 Detects structural damage or missing RAR volumes before any recovery decision
- 📊 Reads metadata blocks without altering the archive — safe for compliance workflows
- 🧭 Differentiates password issues from corruption and format mismatches
- 🖥️ 100% offline — nothing leaves your corporate environment
| What You See | What FileBrio Helps You Verify |
|---|---|
| Archive won’t open | Is it damaged, mis-sequenced, or encrypted-header locked? |
| “Wrong password” alerts | Password issue vs. structural integrity issue |
| No file list displayed | Encrypted headers vs. malformed metadata |
Before moving forward with authorization, get a safe, offline snapshot of the archive’s actual state:
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
📂 Accepted Evidence Types for Encrypted RAR Archives
Organizations typically accept multiple forms of evidence when proving ownership. The stronger the data sensitivity, the more rigorous the documentation must be.
| Evidence Type | Description | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Project documentation | Archive referenced in project briefs, task tickets, or deliverables | Strong |
| Version-control or file-tracking logs | Commit history, folder lineage, or internal upload logs | Strong |
| Internal emails or attachments | File sent or received within corporate accounts | Moderate |
| Employee or contractor notes | Handover files, internal notes, or documented password hints | Moderate |
| Machine metadata | File timestamps, device associations, folder labels | Weak to moderate |
| Oral statements | Employee recollections without supporting documents | Weak |
Storing metadata safely is essential for long-term continuity. Related guidance appears in how teams can organize shared RAR password metadata ↗️.

📜 Building an Audit-Ready Chain of Custody
Compliance teams often require a full chain-of-custody before allowing diagnostic or recovery actions. This includes:
- Creation details — who created the archive, when, and for what purpose.
- Storage path progression — server folders, team directories, or cloud shares.
- Transfer records — how the archive moved across systems or user accounts.
- Access logs — who interacted with the archive and when.
If your archive is corrupted or unreadable, chain-of-custody evidence helps clarify whether recovery is even feasible. High-level guidance can be found in how to stabilize your partially corrupted RAR file ↗️.
👥 Who May Authorize Access (Roles & Responsibilities)
Even if your team uses the archive daily, only certain roles typically have the authority to authorize access or recovery attempts:
- Data owners / department managers
- Information security officers
- Compliance or governance leads
- System administrators (technical custodians)
Authority is tied not to who handles the file but to who is responsible for safeguarding the underlying data.
🏬 Department-Level Scenarios and How Proof Works
To illustrate how corporate ownership proof works, here are common scenarios:
IT Department Archives
IT archives often contain configuration exports, deployment packages, or encrypted backups. Ownership is usually straightforward: the IT department is both the creator and the custodian.
Finance & Accounting Archives
If archives store payroll, tax, or budgeting data, access requires sign-off from senior finance or compliance officers.
Customer or Vendor Project Archives
Ownership typically lies with the project’s managing department. Contracts may also impose additional data-governance obligations.
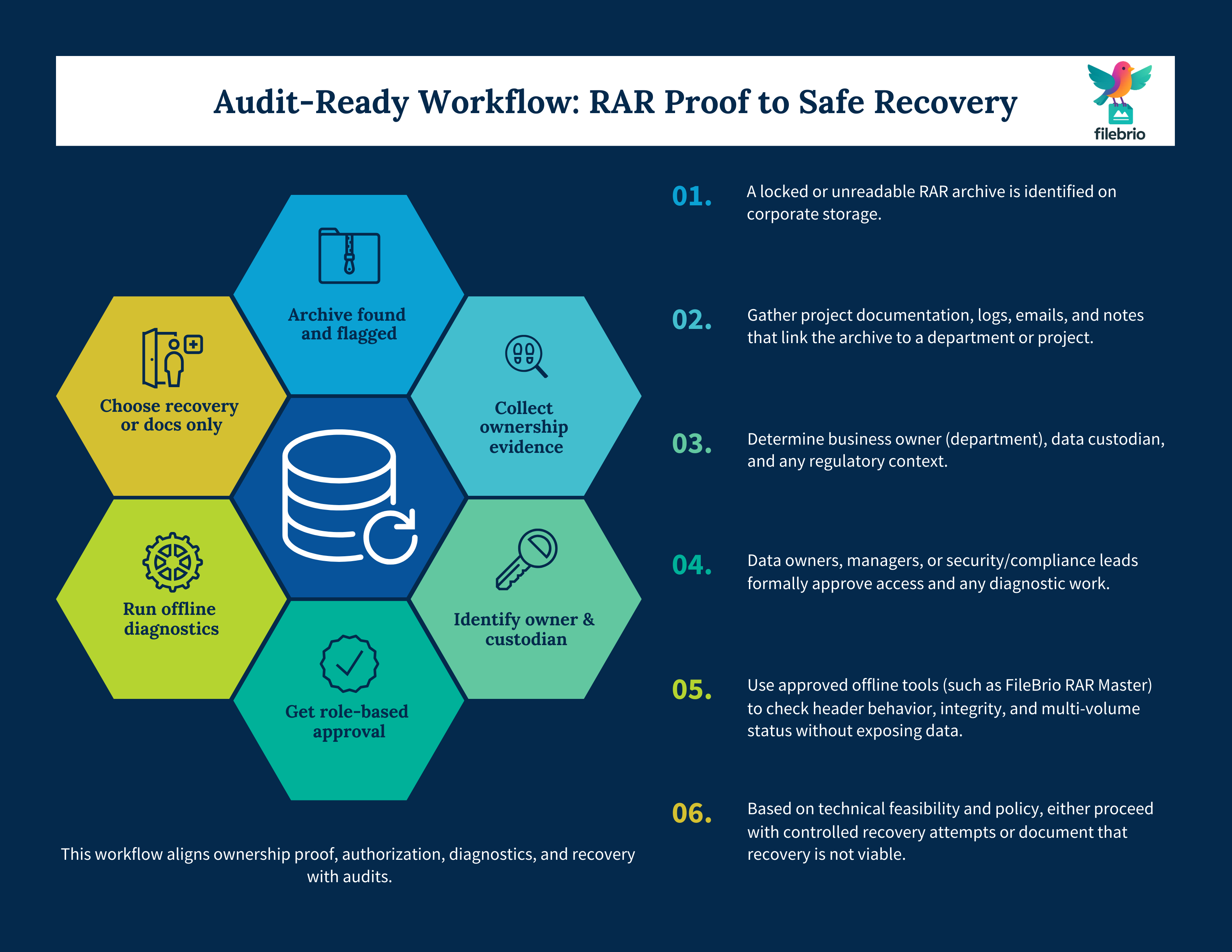
🔒 A Compliance-Safe Path From Ownership Proof to Real, Private Recovery
Once ownership is documented and approved, the next challenge is practical:
Can the archive actually be opened?
Corporate teams often authorize access only to discover that the archive is damaged,
multi-volume parts are missing, or encrypted headers hide all structural clues.
FileBrio RAR Master bridges this gap — giving you a controlled, offline way to evaluate whether recovery
is technically possible before you proceed with password workflows or further chain-of-custody steps.
- 📁 Verifies RAR4/RAR5 integrity without exposing data to external systems
- 🧩 Identifies corruption levels, truncated segments, and broken metadata
- 🔐 Confirms header encryption behavior — critical for regulated environments
- 📂 Validates multi-volume sequences across departmental storage paths
- 🛡️ Keeps sensitive or regulated data fully offline and under audit control
| Your Compliance Workflow | What FileBrio Adds |
|---|---|
| Authorization + ownership proof | Offline confirmation the archive is structurally usable |
| Chain-of-custody documentation | Traceable diagnostics that fit audit requirements |
| Departmental approval | Clear insight into whether password recovery is feasible |
Before teams escalate to security officers or external auditors, ensure the archive is technically sound:
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
📊 Table — Evidence Strength Levels
| Strength Level | Examples | Effect on Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| Strong | Project references, tickets, VCS logs, audit trails | Usually enough for immediate approval |
| Moderate | Handover notes, internal attachments, folder lineage | Often needs a managerial sign-off |
| Weak | Personal recollections, unsupported assumptions | Rarely accepted without supporting evidence |
🛡️ Reducing Risk During Verification
While verifying ownership, it is important to avoid unnecessary exposure of the archive:
- Never upload corporate archives to unknown websites.
- Perform checks only on organizationally approved hardware.
- Ensure that all actions are logged for audit purposes.
Offline verification is especially important, as explained in why offline tools keep your encrypted RAR data private ↗️.
🔄 Preventing Ownership Confusion in the Future
Organizations can eliminate many future access issues by establishing consistent policies:
- Use standardized naming conventions.
- Store metadata that identifies owning departments.
- Maintain an internal password-metadata system for RAR archives.
- Document archive lifecycle events (creation, transfer, archival, deletion).
Team-level guidance for this appears in safe ways to distribute password notes for your team’s RAR files ↗️.
🧾 When Corporate Security Teams or External Auditors Get Involved
For high-sensitivity archives — especially those containing customer data or regulated materials — corporate policy may require escalation to:
- internal security operations teams,
- compliance auditors, or
- external forensic specialists (under NDA).
These teams will demand documented ownership, purpose, and history before authorizing any recovery effort.
📜 Legal Reminder
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📚 See Also
- How to Prove Ownership of a RAR Archive in Corporate Environments ↗️
- How Teams Should Store RAR Password Metadata Safely Across Devices and Roles ↗️
- Legal Considerations When Working With Your Own Encrypted Archives ↗️
- Why Offline Recovery Tools Are Safer for Privacy ↗️
- How to Diagnose a Locked RAR Archive Without Risking Data Loss ↗️
- How to Strengthen RAR Archive Security While Preserving Future Access ↗️