
How to Prevent RAR Data Loss on USB Drives, HDDs, and Cloud Storage
You copy a carefully prepared RAR backup to a USB stick, send another copy to cloud storage, and leave a third one on an external HDD — and still, years later, one of them refuses to open or reports damage. Maybe it was unplugged too early, maybe a sync conflict silently overwrote your file, or maybe a slowly dying disk corrupted just the wrong sectors.
If your RAR archives hold project work, private photos, or corporate records, even a single unreadable backup can feel like a serious failure. At the same time, you might be unsure which habits actually protect your archives and which “safety rituals” are just superstition. Is cloud storage enough? Are two USB copies safe? How often should you verify old backups?
This article gives you a practical, technology-agnostic strategy for keeping your own RAR archives safe across USB drives, HDDs/SSDs, and cloud services. The focus is on prevention: building resilient backup sets, catching early warning signs, and using offline, privacy-first tools to verify and repair problems when they appear.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📌 TL;DR — Quick Overview of RAR Data-Loss Prevention
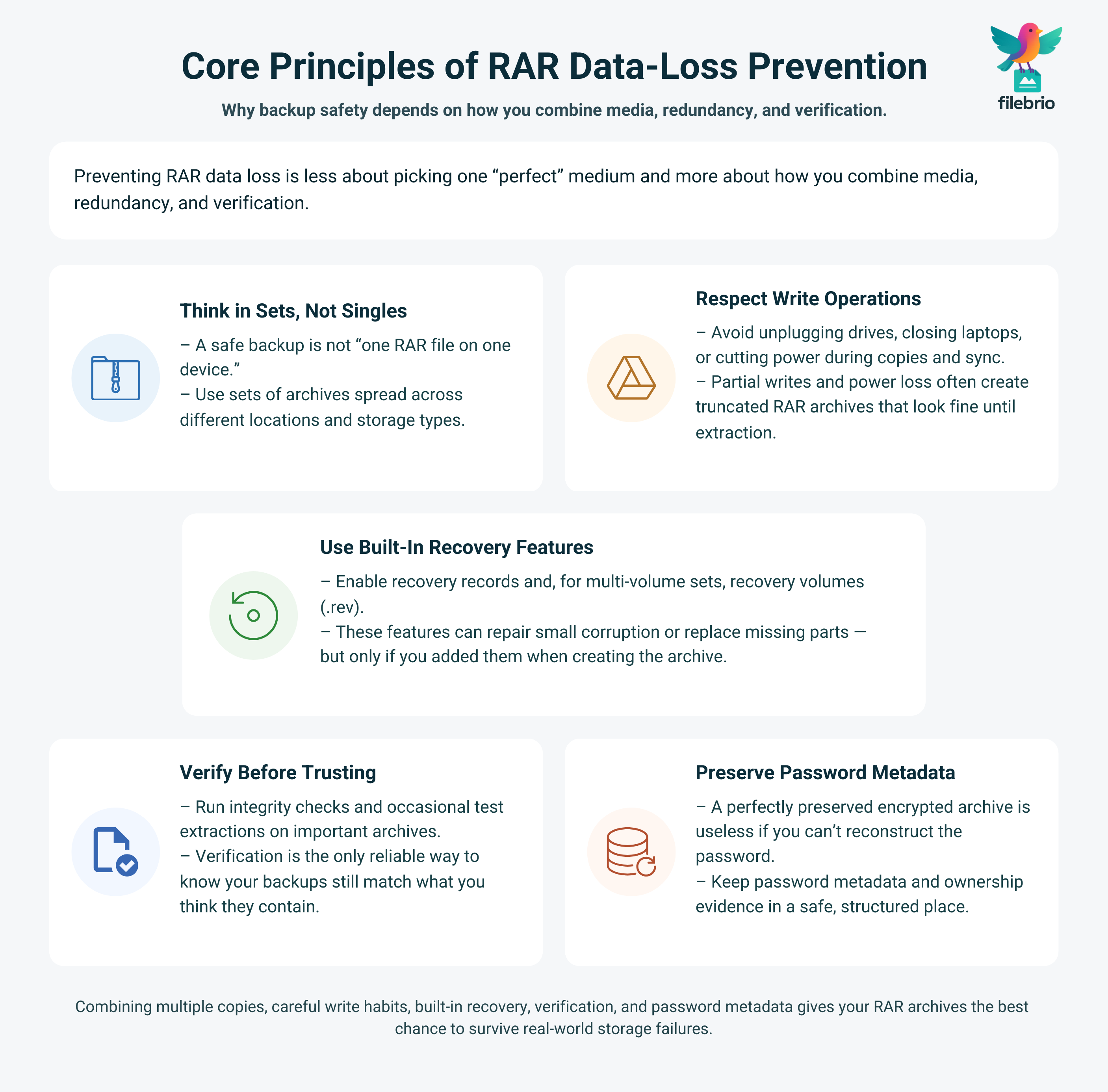
If a RAR archive is the only copy of your data, you are one accident away from losing it. USB drives can be unplugged mid-write, HDDs and SSDs wear out, and cloud storage can silently replace a good file with a partial one after a sync conflict. Preventing RAR data loss is less about any single “magic” medium and more about how you combine media, redundancy, and verification.
- Think in sets, not singles. A safe RAR backup is not “one file on one device” but a set of archives spread across different locations and technologies.
- Respect write operations. Interrupting copies, yanking USB sticks, or closing laptops during sync creates truncated archives that may look fine until you try to open them months later.
- Use built-in resilience. Recovery records and recovery volumes can help when individual volumes are damaged, but they only work if you enable them when creating the archive.
- Verify before trusting. Integrity checks and occasional test extractions are the only reliable way to know whether your RAR backups still match what you think they contain.
- Don’t forget password metadata. A perfectly preserved encrypted archive is still useless if you cannot reconstruct the password or prove ownership when needed.
Across USB, HDD/SSD, and cloud, the most reliable strategy is a layered approach: at least two independent copies, stored on different media, with recovery features enabled, and verified on a predictable schedule. Add an offline, privacy-first toolkit for diagnostics and repair, and you drastically reduce the chance that a single failure — or a quiet sync glitch — will cost you your data.
🧠 Why RAR Archives Get Lost or Corrupted Across Different Storage Types
To prevent data loss, it helps to understand why archives disappear or become unreadable in the first place. Different storage technologies fail in different ways, but many incidents share the same patterns:
- Partial writes and power loss. A system crash or power cut during archive creation or copying leaves you with an incomplete file that may not show obvious signs until extraction time.
- Silent bit rot. On aging HDDs or consumer-grade NAS devices, rarely accessed files can slowly accumulate errors, eventually breaking the archive structure.
- Human error. Deleting, renaming, or moving a single part of a multi-volume set can make the whole archive unusable.
- Cloud sync conflicts. When multiple devices modify or upload the same file, some providers replace a good copy with a truncated or partially uploaded one.
RAR itself provides several mechanisms to resist these realities — including recovery records and dedicated recovery volumes — but they need to be planned in from the start. A high-level overview like how recovery records safeguard your damaged RAR files ↗️ shows how these features can protect you from small-scale corruption and missing volumes when properly configured.
At the same time, there is a balance to strike: adding more redundancy can increase archive size and storage costs. Guidance such as how to strengthen RAR archive security while preserving future access ↗️ can help you design archives that are both robust and realistically maintainable over years of hardware and platform changes.
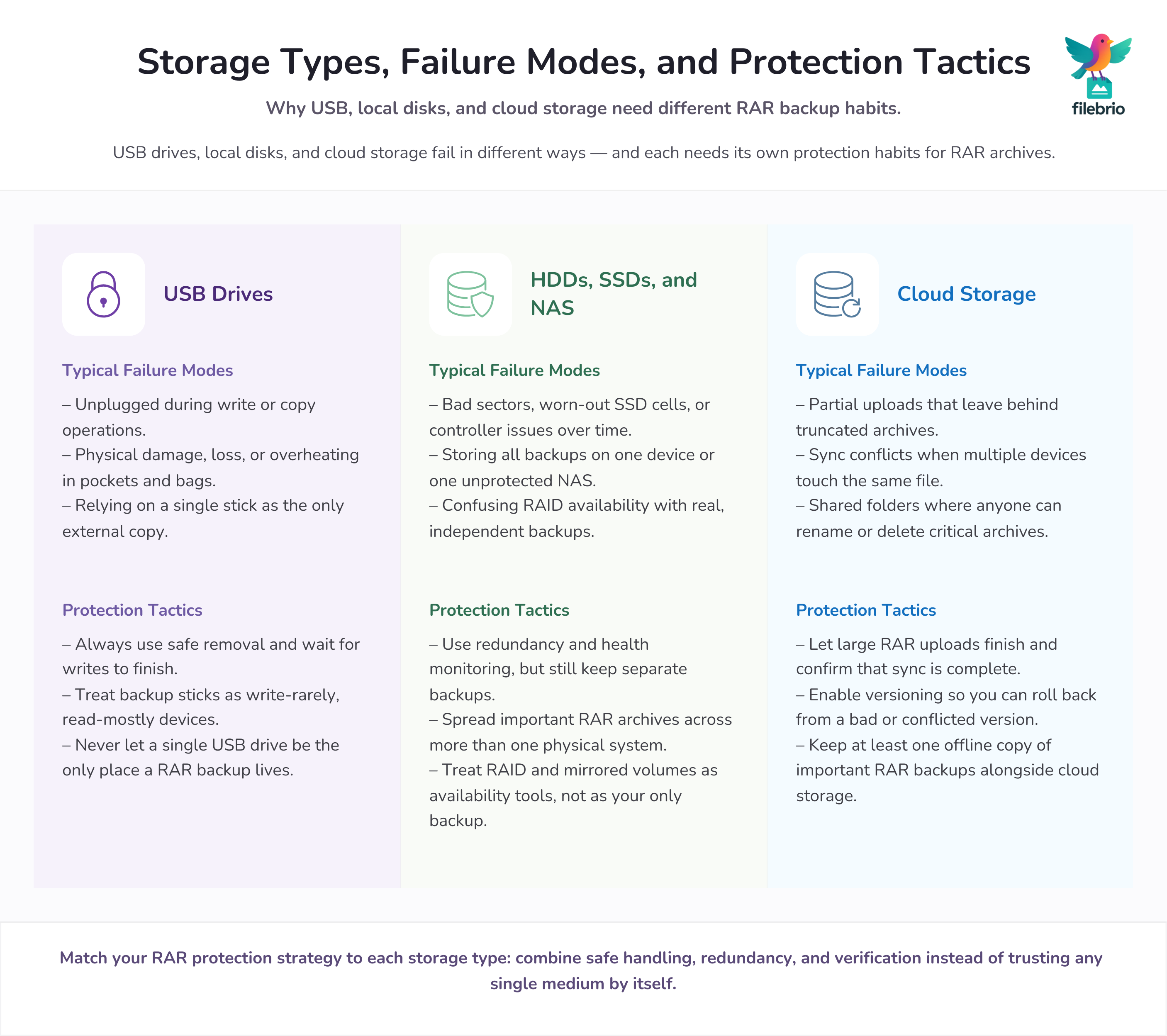
🔌 USB Drives: Safe Handling and Common Failure Traps
USB sticks are ubiquitous, cheap, and incredibly convenient — which is exactly why they feature in so many data-loss stories. They are often used for quick copies, temporary handoffs, or “just in case” backups, but they are also easy to lose, mis-handle, or physically damage.
Typical USB-related risks include:
- Unplugging the drive before write operations have fully completed.
- Using the same stick across many machines without safely ejecting it.
- Relying on a single USB device for the only external copy of a RAR backup.
- Leaving sticks in hot environments, pockets, or bags where they are bent or crushed.
To keep RAR archives safer on USB devices:
- Always eject properly. Wait for writes to finish and use the operating system’s safe removal function to flush caches before unplugging.
- Prefer one-way usage. Treat a “backup” stick as write-rarely, read-mostly. The more you write, the more chances for interruption and corruption.
- Avoid single-stick strategy. If a RAR archive matters, never let a single USB drive be its only external home.
USB backups work best as part of a broader plan: for long-term archives or decade-old projects, consider pairing them with more stable storage and migration strategies described in how to preserve access to your decade-old RAR files ↗️, so that a single misplaced or corrupted stick doesn’t become a single point of failure.
💽 HDDs, SSDs, and NAS Storage: Long-Term Health for RAR Backups
Hard drives, SSDs, and network-attached storage (NAS) offer more capacity and better performance than USB sticks, but they introduce their own failure patterns. Spinning HDDs may develop bad sectors; SSDs have finite write endurance; some NAS units are configured without adequate redundancy or monitoring.
Key practices for RAR backups on HDD/SSD/NAS:
- Use redundancy where appropriate. RAID and mirrored volumes protect against single-disk failure, but they are not a backup by themselves — they mainly improve availability and reduce the impact of individual hardware faults.
- Monitor SMART and health metrics. Many drives report early warning signs. When you see repeated reallocation events or read errors, prioritize copying RAR archives off those devices.
- Avoid “one big basket” designs. Keeping all backups on a single NAS without an external copy exposes you to theft, fire, ransomware, or catastrophic controller failure.
Large RAR archives — such as long-term project bundles or multi-volume collections — need extra care. Recommendations in how to manage large RAR files without risking data ↗️ help you plan around long extraction times, fragmentation, and the risk that a single damaged sector can impact many gigabytes of compressed data.
Over the lifetime of a drive, you will eventually move archives between devices or storage tiers. When you do, it is wise to treat these moves as opportunities to modernize archive formats, as discussed in safe practices for migrating your older RAR contents ↗️. Converting old RAR sets to modern RAR5 archives with updated recovery options often pays off years later when you need to access them again.
☁️ Cloud Storage: Sync Conflicts, Versioning, and Safe Sharing
Cloud storage adds genuine resilience — your RAR file is no longer tied to a single device — but it also introduces new failure modes that don’t exist on standalone disks. Two devices uploading different versions, incomplete syncs on unstable networks, and aggressive deduplication policies can all harm archives if you are not careful.
Common cloud-related pitfalls for RAR archives:
- Partial uploads. A file may appear in the cloud but actually be a truncated upload that never completed successfully.
- Sync conflicts. Renaming, moving, or editing a local copy while another device is still syncing can lead to competing versions — sometimes the wrong one “wins”.
- Shared folders without clear ownership. When multiple people can rename or delete files, it becomes harder to ensure archive continuity.
To reduce risk:
- Allow sync to finish before disconnecting. For large RAR archives, confirm that the cloud client reports a completed upload, not just “uploading…”
- Use versioning features. Many providers let you restore earlier file versions, which can rescue you from a sync conflict that replaced a healthy archive with a damaged one.
- Keep at least one offline copy. Cloud should complement, not replace, your local backups — especially for sensitive or business-critical archives.
For sensitive archives, pairing cloud storage with a strong, well-documented encryption and access strategy makes a big difference. Concepts from how to strengthen RAR archive security while preserving future access ↗️ show how to keep archives private while still ensuring that future you (or your team) can reliably decrypt and use them.
💼 All-In-One Toolkit to Centralize Safe RAR Handling
When your RAR archives live on multiple USB drives, disks, and cloud accounts, one of the biggest risks is inconsistent handling. Different people use different tools, some archives are tested and others are not, and nobody is quite sure which copy is the “good” one anymore.
FileBrio RAR Master, as part of the FileBrio Office Suite, is designed to give you a centralized, offline environment for working with your own RAR archives safely and consistently:
| Need | Typical Risk Without a Unified Tool | How FileBrio RAR Master Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect archive health before moving to new storage | Copying silently corrupted archives between devices | Use structure-aware diagnostics to confirm health first |
| Standardize repair and verification steps | Ad-hoc tools and habits that vary by user | Repeatable workflows built around one RAR-focused toolkit |
| Protect confidential archives during checks | Uploading sensitive data to “free online repair” services | 100% local processing on Windows, fully offline |
Instead of guessing whether a backup is still valid, you can integrate health checks into your storage routine, then log those results for future audits. For technical teams, this can be aligned with a broader plan that includes parity and recovery data, as described in RAR Recovery Records and .rev Volumes: How They Help Protect and Restore Data ↗️, and resilient security design, as in how to strengthen RAR archive security while preserving future access ↗️. When you are ready to build this into your workflow, you can explore the FileBrio RAR Master features ↗️ that focus on diagnostics, repair, and offline handling for your own encrypted archives.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
🔍 Monitoring, Integrity Checks, and Early Warning Signs
Even the best storage setup can fail silently if you never look at your backups again. Integrity checks and occasional test extractions are your early-warning system — the way you discover problems while you still have time and options.
Useful monitoring steps include:
- Checksum or hash verification. Keeping separate hashes for critical RAR files lets you detect any bit-level changes over time.
- Periodic test extractions. For your most important archives, occasionally performing a full or partial extraction on fresh hardware confirms that both storage and archive structures are healthy.
- SMART and log review. Storage systems often report developing issues long before complete failure. Combine drive health monitoring with a list of which RAR archives live where.
When you do access an archive after a long time, it is wise to verify not just that it opens, but that the extracted data is correct. The high-level approach in how to verify file integrity after successfully accessing a RAR archive ↗️ shows how to check that your recovered files are complete and uncorrupted, rather than relying on a quick glance at filenames.
Monitoring is not just about catching catastrophic failures; it also helps you spot trends. If you see that older disks or certain USB sticks repeatedly generate minor errors, you can prioritize migrating affected archives sooner rather than later.
🧩 Workflows, Documentation, and Team Practices
Technical measures alone cannot guarantee safety if your workflow is chaotic. Teams that handle RAR archives across many devices and people need clear, shared practices. Otherwise, one colleague might store the “final” archive on a personal USB stick, while another assumes it is in cloud storage — and nobody realizes the gap until much later.
Elements of a resilient RAR workflow:
- Defined locations. Decide where “authoritative” copies of important archives live: which servers, which cloud folders, which external drives.
- Documented procedures. Write down how new archives are created, how recovery options are configured, and how many copies are required before a project is considered backed up.
- Ownership and roles. Clarify who is responsible for long-term access, who runs periodic integrity checks, and who is allowed to delete or archive old RAR files.
Storing references and password metadata in a safe, structured way is part of this picture. A personal practice inspired by how to organize metadata for your RAR passwords safely ↗️ might cover your own archives, while team-level approaches like how to safely store RAR password metadata for future access ↗️ and how to maintain long-term access to encrypted RAR archives (teams & enterprises) ↗️ help organizations avoid losing access when staff change roles or leave.
Good documentation also makes it easier to prove that you are working with archives you legitimately own and control, which matters for both compliance and collaboration with external partners.
🛡️ Secure Offline Solution for Critical RAR Archives
Some RAR archives are more than just convenience; they are business records, legal evidence, or irreplaceable personal material. For those, relying on random tools or untrusted online services is simply not acceptable. You need a controlled, auditable environment that respects both encryption strength and privacy.
FileBrio RAR Master is built for exactly this kind of offline, privacy-first scenario. Instead of scattering your efforts across multiple utilities and websites, you can rely on a single toolkit that stays on your own machines:
- Use structure-aware diagnostics and modules similar in spirit to repair damaged RAR archives ↗️ to understand what went wrong without exposing data to third parties.
- Plan safe recovery and migration steps while comparing offline vs online RAR recovery ↗️, so you can justify keeping sensitive archives entirely in-house.
- Align your usage with policy and compliance, supported by centralized guidance like legal and responsible use policy ↗️ and transparent FileBrio user reviews that demonstrate how others deploy the tools.
By standardizing on a single offline toolkit for RAR handling, you reduce the risk that someone will upload a critical archive to an unknown site “just this once” — and you make it much easier to train staff on safe procedures. When you are ready to integrate this into your environment, you can obtain the installer directly from the official FileBrio downloads ↗️ page and roll it out on managed workstations.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
🛠️ Practical Checklist: Building Resilient RAR Backup Sets
To turn all of these ideas into concrete practice, it helps to keep a simple checklist. You can adapt the following points to your own environment and risk tolerance.
- Multiple copies: For important archives, keep at least two independent copies on different media (for example, local disk + cloud, or NAS + offline USB).
- Recovery features: When creating multi-volume archives, enable recovery records and consider adding recovery volumes, as explained in how recovery records safeguard your damaged RAR files ↗️.
- Format modernization: Migrate older RAR sets to modern formats as described in safe practices for migrating your older RAR contents ↗️, especially when you refresh hardware or storage platforms.
- Storage hygiene: Follow advice similar to ways to prevent losing your RAR data on storage devices ↗️ and best practices for managing large RAR archives safely ↗️ when dealing with large or long-lived backups.
- Integrity checks: Periodically validate key archives using the principles in how to verify file integrity after successfully accessing a RAR archive ↗️, and record your results.
- Password metadata: Maintain secure references based on how to organize metadata for your RAR passwords safely ↗️ and how to safely store RAR password metadata for future access ↗️, so you don’t lock yourself out of perfectly healthy archives.
- Team coordination: If multiple people manage archives, design policies along the lines of how to maintain long-term access to encrypted RAR archives (teams & enterprises) ↗️, so ownership and responsibilities remain clear.
Over time, these habits become routine. Instead of reacting to failures, you build a storage environment where RAR data loss is rare, limited in impact, and easier to diagnose when it does occur.

📜 Legal Reminder: Working Only With Archives You’re Entitled to Use
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
🔗 See Also: Learn More About RAR Safety and Recovery
- What to Do When WinRAR Shows ‘Unexpected End of Archive’ ↗️
- How to Check the Internal Structure of RAR Archives Without Extracting Files ↗️
- Lost Your RAR/WinRAR Password? How to Assess Your Situation Before Taking Action ↗️
- How to Avoid Losing Access to Decade-Old RAR Archives ↗️
- Why Old RAR4 Archives Still Matter — and When to Convert Them ↗️
- Open RAR Files Without a Password? What’s Possible, What Isn’t, and How to Access Your Data Safely ↗️
- Extracting RAR/WinRAR Files With or Without a Password: Safe Techniques for Handling Locked Archives ↗️