
How to Maintain Long-Term Access to Encrypted RAR Archives (Teams & Enterprises)
Encrypted RAR archives are widely used in organizations for protecting sensitive data — financial documents, engineering assets, source code deliveries, legal materials, medical files, and more. But strong protection comes with a hidden operational risk: if even one key holder leaves, forgets their password, or mismanages storage, an entire department’s historical data can become permanently inaccessible.
Enterprises face an additional challenge: access must be both secure and sustainable across teams, devices, and years — sometimes decades. This article explains how to build a long-term, role-based retention strategy for encrypted RAR archives so that your organization never experiences irreversible data loss, regulatory problems, or workflow disruptions due to missing credentials or lost metadata.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📌 TL;DR — Long-Term Access to Encrypted RAR Archives
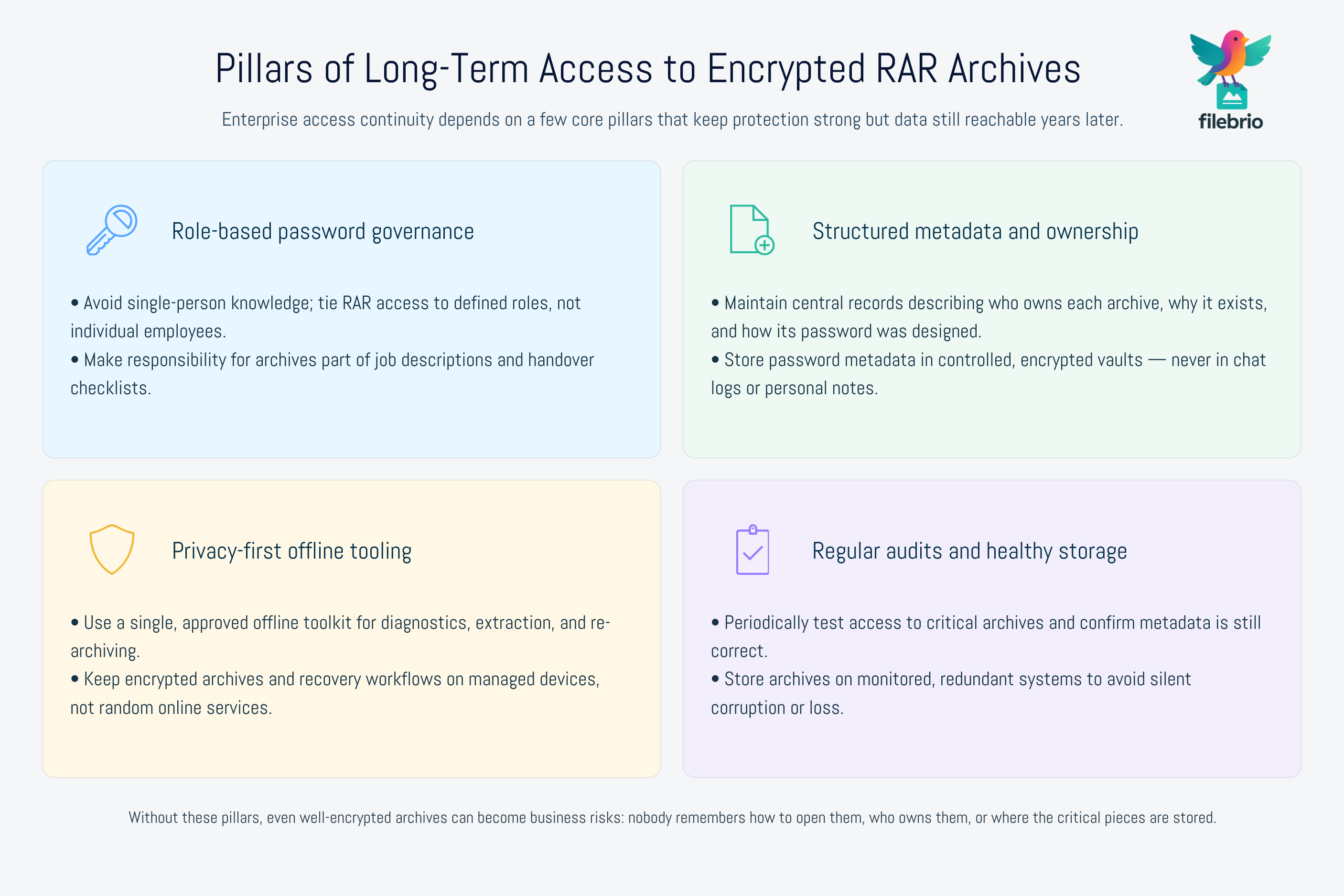
Long-term, multi-role access to encrypted RAR files is not automatic. Encryption protects business-critical content, but it also means losing the password equals losing the data. Enterprises need durable processes that outlive staff, devices, and departmental reorganizations.
To maintain continuity:
- Build a role-based password governance model so knowledge doesn’t concentrate in one person’s head.
- Securely store RAR password metadata using offline, access-controlled vaults — not cloud notes or emails.
- Use structured recovery workflows so extraction, verification, and re-encryption follow predictable steps.
- Document ownership and responsibility for each encrypted archive or archive group.
- Periodically audit stored archives to ensure passwords, metadata, and access policies remain accurate.
- Prefer privacy-first, fully offline tooling to avoid data leaks, lockouts, or exposure.
Teams that implement these principles avoid the common pitfalls: forgotten passwords, missing ownership records, lost metadata, and unnecessary recreation of critical business files.
⚠️ Why Long-Term Access Fails in Teams and Enterprises
RAR archives provide excellent protection — but organizations frequently underestimate how fragile long-term access becomes if processes are informal. Some of the most common failure points include:
- Single-person password knowledge — one administrator leaves, and a decade of departmental data becomes inaccessible.
- Scattered storage of notes — passwords saved in chat logs, notebooks, old employee emails, or personal devices.
- Lack of central ownership — no documented responsible party for each archive or project.
- No metadata retention system — teams forget why an archive was created or how its password was chosen.
- Informal naming conventions — file names that give no context and age poorly.
- Policy gaps during staff turnover — archives remain unassigned, untracked, and effectively orphaned.
To avoid these risks, some enterprises adopt structured diagnostics similar to safe methods for diagnosing locked RAR files ↗️, but broadened for an organizational setting. Instead of reacting at the moment of crisis, they plan for long-term continuity from day one.
🧠 Key Factors That Influence Multi-Year RAR Accessibility
Maintaining long-term access to encrypted RAR archives requires predictable systems that stand the test of time. Several technical and organizational factors determine whether archives remain usable years later:
1. Password Design Quality
Weak passwords risk exposure; overly complex ones risk being forgotten. Teams benefit from approaches similar to understanding how memory cues influence password design ↗️ to create patterns that are both secure and manageable.
2. Format Longevity (RAR4 vs RAR5)
RAR5 includes stronger cryptography and metadata handling. Archives created long ago with RAR4 may lack resilience features. For corporate datasets, understanding format differences — and eventually migrating old archives — is essential.
(If RAR4 archives are part of your workflow, evaluating their long-term viability aligns with themes in safe conversion of older RAR files ↗️.)
3. Storage Integrity
Hard drives, NAS systems, cloud storage, and USB drives all degrade differently over time. Poor storage environments lead to corrupted archives, making access difficult even with the correct password. Guidance such as how to prevent RAR data loss across storage devices ↗️ is particularly relevant for multi-year retention.
4. Organizational Memory
Corporate archives outlive staff, projects, and even entire departments. Long-term access relies heavily on:
- Clear documentation
- Centralized custody
- Structured password metadata
- Versioned access records
Without these, even properly stored encrypted files become unusable because no one remembers how they were protected or why they were created.
💼 All-in-One Workspace for Enterprise RAR Access Continuity
Enterprise workflows often involve dozens or hundreds of encrypted archives — backups, project exports, sensitive handovers, confidential deliverables. Managing them with ad-hoc tools is inefficient and risky.
FileBrio RAR Master centralizes diagnostics, extraction, repair, and metadata review into a single, offline environment. This helps corporate administrators and multi-role teams:
- Verify archive health before accessing or transferring files.
- Inspect metadata, structure, and encrypted headers.
- Handle damaged or partially corrupted archives safely.
- Maintain access continuity through standardized procedures.
When paired with organizational policy and proper metadata governance, the toolkit helps teams avoid the biggest long-term access risks.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
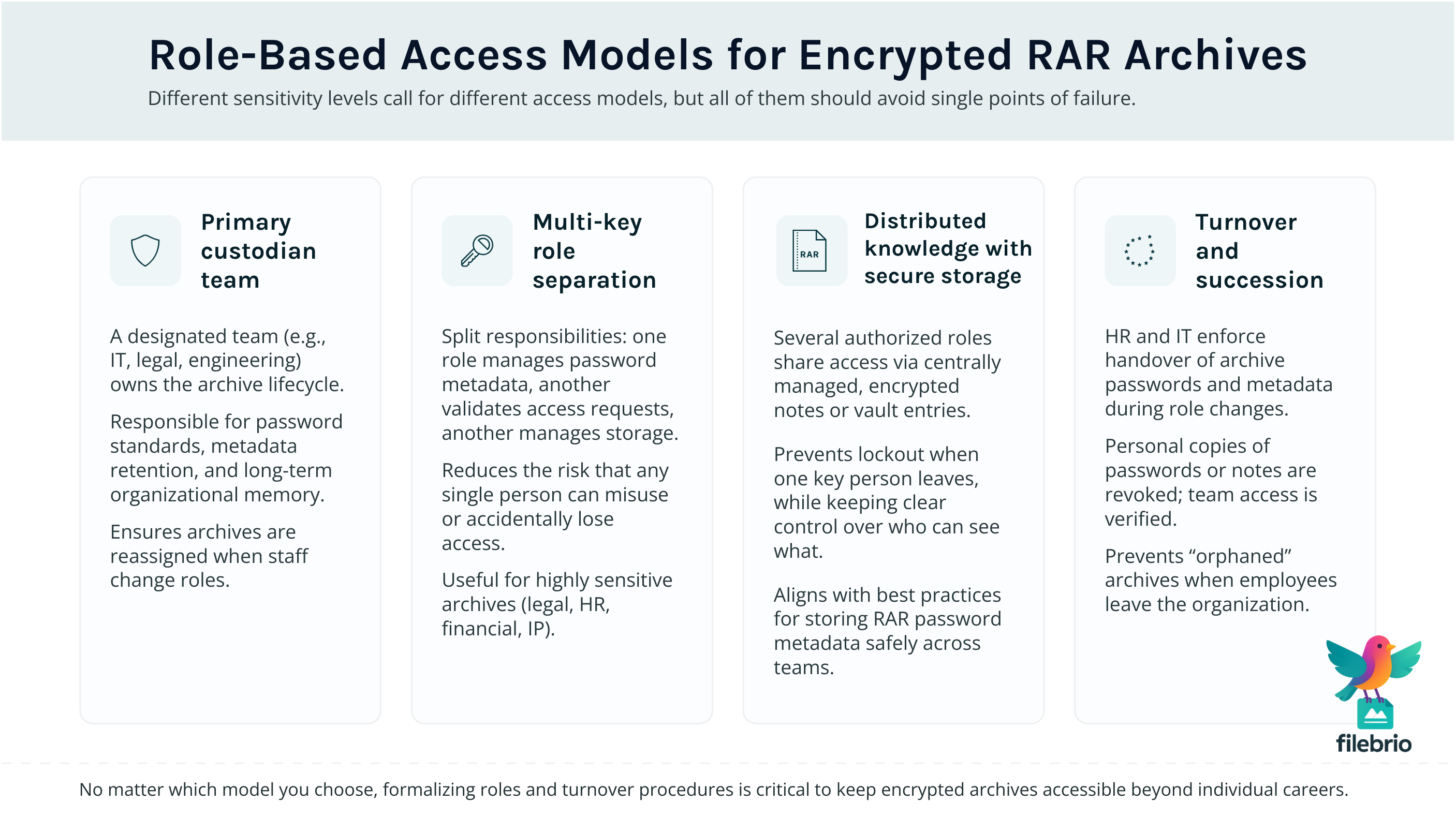
👥 Role-Based Access Models for Your Encrypted RAR Archives
A core component of long-term access planning is preventing any single point of failure. Teams should adopt role-based structures where access to encrypted archives is tied to defined responsibilities rather than individual employees.
1. Primary Custodian Model
One team owns the archive (IT, legal, engineering). They handle:
- Password creation standards
- Metadata retention
- Organizational memory
- Turnover transitions
2. Multi-Key Role Separation
For highly sensitive archives, responsibilities can be split:
- One role stores the password metadata.
- Another role validates access requests.
- A third role manages archive storage and backups.
This separation ensures no single person has total control while still guaranteeing recoverability.
3. Distributed Knowledge with Secure Storage
When several departments rely on the same archive, you can distribute encrypted notes or password metadata so that multiple authorized roles retain access even if one person leaves. Teams working with shared archives often benefit from methodologies described in how teams should store RAR password metadata safely ↗️.
4. Turnover & Succession Procedures
Human resource policies should require:
- Transfer of all archive passwords and metadata upon role changes
- Revocation of personal storage or notes
- Verification that team access remains intact
This prevents corporate lockouts — a surprisingly common issue in long-running projects.
📁 Metadata, Ownership Records & Organizational Memory
Encrypted RAR archives require more than just passwords to remain usable. You also need a durable metadata layer that captures:
- Why the archive was created
- Who owns it
- What it contains (high-level description)
- Password creation patterns or guidelines
- Creation dates and retention timelines
- Related systems or project identifiers
Organizations with structured metadata practices suffer far fewer lockouts. This aligns with best practices discussed in storing personal RAR password metadata safely ↗️, extended here to enterprise scale.
🛡️ Secure Offline Tooling for Institutional Continuity
Enterprises should avoid online tools for managing, extracting, or diagnosing encrypted RAR archives. Cloud-based access introduces unnecessary risk and weakens compliance posture. A privacy-first, audit-friendly workflow requires everything to remain local.
FileBrio RAR Master supports this approach by providing:
- Zero-upload, fully offline operation
- Diagnostic tools for encrypted headers
- Safe repair options for damaged archives
- Metadata visibility to maintain long-term continuity
When archives are damaged, corporate workflows often rely on the corrupted archive repair ↗️ capability, followed by integrity checks. Administrators access the official FileBrio Office Suite download page ↗️ to maintain compliant, standardized installations.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
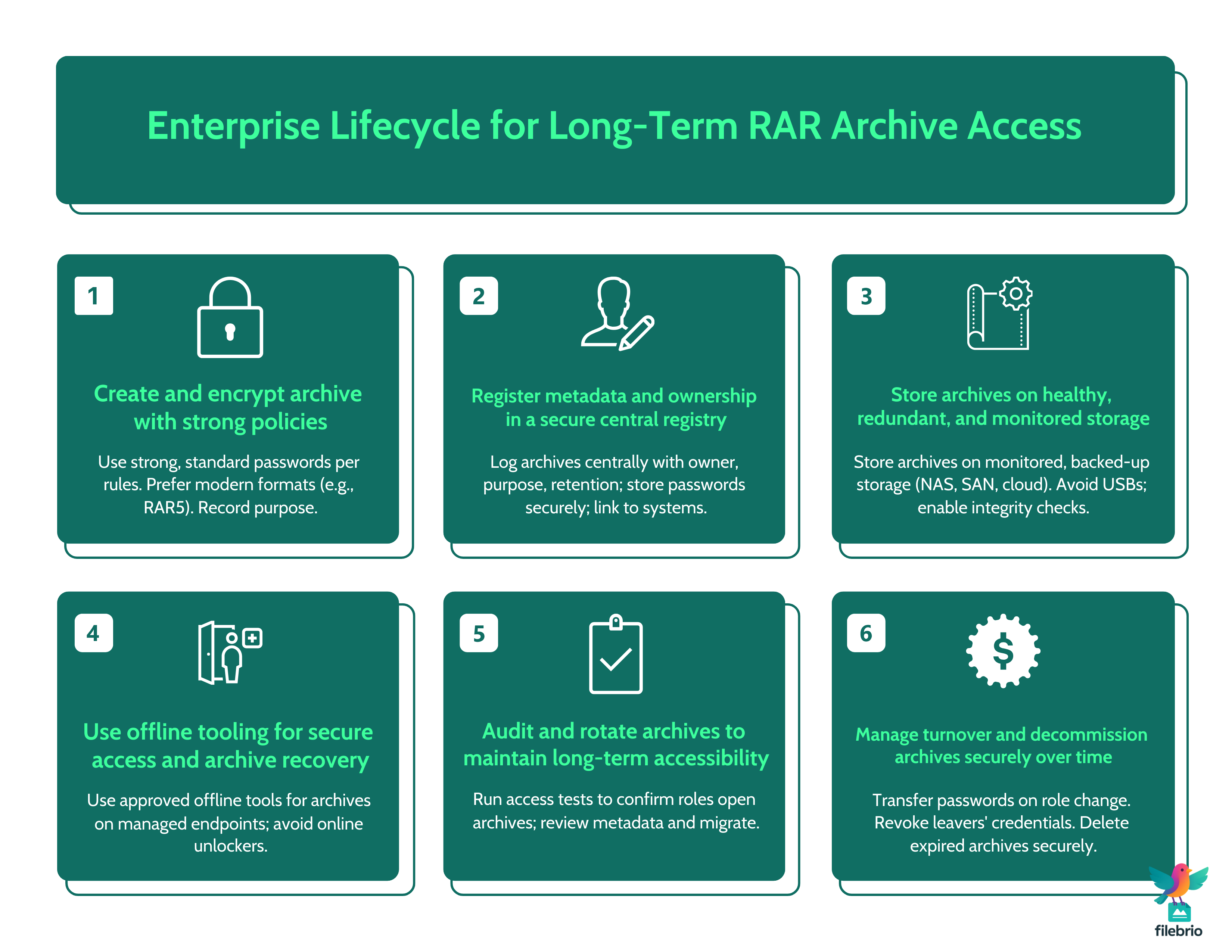
📈 Long-Term Protection: Prevention, Storage, and Policy
Achieving stable, predictable RAR access over years requires combining technical safeguards with clear internal policy.
1. Storage Health Monitoring
Archives should be stored on validated, redundant systems with monitoring and regular checks. Accidental corruption is most effectively prevented through disciplined storage practices.
2. Archive Versioning
Maintain versioned backups so teams can restore earlier states if corruption goes unnoticed for long periods.
3. Consistent Password Policies
Password consistency prevents fragmentation and forgotten patterns. Corporate-wide standards help all departments maintain predictable long-term access.
4. Periodic Access Testing
Annual or quarterly RAR access reviews help verify:
- Metadata accuracy
- Password validity
- Retention timelines
- Access continuity across team roles
Regular validation mirrors the forward-looking principles found in enterprise continuity planning ↗️ itself — ensuring no archive becomes an unintentional risk.
⚖️ Legal Reminder and Responsible Use
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
🔗 See Also: Enterprise RAR Management Guides
- How to Avoid Losing Access to Decade-Old RAR Archives ↗️
- Why Old RAR4 Archives Still Matter — and When to Convert Them ↗️
- How to Create Password Policies for RAR Archives in Business Settings ↗️
- How to Document Ownership of Sensitive Encrypted Archives ↗️
- How to Share Encrypted RAR Files Safely with Colleagues or Clients ↗️
- Why RAR5 is More Secure — and What That Means for File Access ↗️