
Legal Considerations When Working With Your Own Encrypted Archives
Encrypted archives carry legal expectations as much as technical ones. Even when you are working strictly with files you own, the way you handle access, diagnostics, and recovery attempts matters. Encrypted RAR/WinRAR archives are designed to restrict visibility, and that restriction has legal weight: only the rightful owner or an authorized party is permitted to inspect, recover, or modify them. Missteps such as uploading encrypted files to unknown online services, bypassing internal approval workflows, or failing to document your actions can create avoidable privacy, compliance, or organizational risks.
This guide provides a high-level, practical framework for navigating those boundaries safely. You’ll learn how to demonstrate ownership, why documentation protects you, how corporate and personal environments differ, and why offline, local diagnostics are essential for privacy. The goal is not to complicate your workflow—it is to ensure that when you access your own encrypted data, you remain legally aligned, audit-ready, and fully in control of where your sensitive information goes.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
📝 TL;DR
Encrypted RAR/WinRAR archives contain sensitive materials by design, and even when you are working strictly with files you own, it is important to stay aligned with lawful handling, responsible documentation, and respect for privacy boundaries. You cannot “reset” or force open a RAR password the way you would with an email or online account, and legal frameworks assume that only the rightful owner may attempt recovery, diagnostics, or repair.
This means you should maintain clear evidence of ownership such as timestamps, project logs, or business documentation; understand that accessing a corporate archive may require approval or documented authorization; avoid exposing encrypted archives to online tools; and rely on local, offline methods to prevent disclosure of protected data. When archives appear damaged or inaccessible, it is also important to identify whether you are facing a password mismatch, corruption, or format limitation before taking action. Using privacy-first tools that keep all operations on your device significantly reduces legal and compliance risks compared to uploading the archive to external sites.
Safe, lawful handling also includes maintaining internal notes about the steps taken, documenting who accessed the archive and why, and following organizational guidelines when working with corporate materials. The purpose is not to complicate your workflow; rather, it ensures that when you access your own encrypted content, you remain protected from compliance misunderstandings, data leakage risks, or misinterpretation of intent. Approached correctly, legal-conscious handling preserves both data confidentiality and your own credibility as the rightful archivist or user.
⚖️ Why Legal Considerations Matter for Encrypted Archives
Handling encrypted archives is not just about cryptography — it is also about rights, ownership, and documented purpose. Unlike ordinary files, encrypted archives contain content whose visibility depends entirely on having a correct password. This gating mechanism has legal weight: it signals that the material is intentionally restricted. Even when the archive belongs to you, taking the right steps protects you from accidental violations of privacy or internal policy rules.
The legal context is especially important in environments where archives circulate across:
- personal devices,
- team storage systems,
- shared drives,
- archival servers,
- cloud sync folders.
This has a direct relationship to guidance such as steps to verify ownership before accessing your RAR file ↗️, which emphasizes that access must always align with lawful rights.
🪪 Ownership Basics: Showing the Archive Is Yours
Ownership is the foundation of legal RAR handling. Even if you know that the archive is yours, an outside observer — a colleague, an auditor, or a compliance officer — does not know this unless you can demonstrate it clearly.
Common forms of valid ownership evidence include:
- File creation timestamps that match your account or system.
- Project documentation referencing the archive.
- Email correspondence showing that you created or received it legitimately.
- Backup logs or versioning histories.
- Internal task trackers referencing the archive name.
Corporate environments typically apply more formal rules, similar to those described in ways to document ownership of your encrypted RAR file ↗️. Following these expectations prevents any misunderstanding that you may be accessing materials outside your scope of authority.
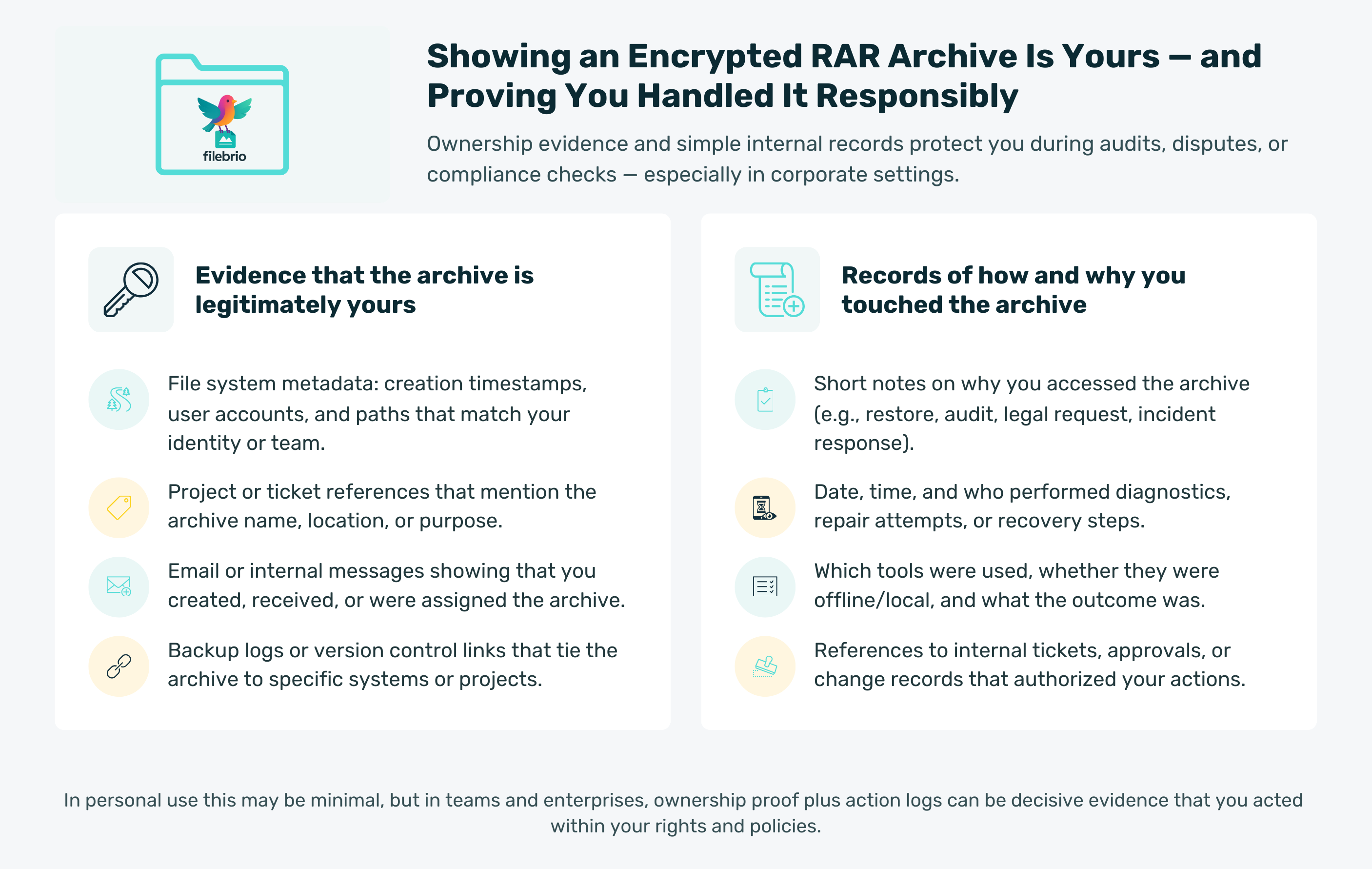
🗂️ Documentation and Internal Recordkeeping
When dealing with sensitive archives, especially in corporate or project-oriented contexts, documenting your activity protects both you and the organization. Well-kept documentation can include:
- Why you accessed the archive
- When you performed diagnostic or recovery actions
- What tool you used
- Whether the access succeeded or remained blocked
This is not bureaucratic overhead. Proper notes act as protective evidence that your actions were responsible and aligned with organizational guidelines. Many legal frameworks expect this level of accountability when working with encrypted materials.
Metadata inspection, such as explained in ways metadata reveals issues in your protected contents ↗️, can be part of that documentation — it shows that you assessed the archive before attempting anything irreversible.
📜 Compliance in Personal, Corporate, and Mixed Environments
Compliance requirements vary by context. Personal archives are usually straightforward: you are the owner, custodian, and decision maker. But the landscape changes in business, institutional, or shared-team environments.
There are three broad compliance categories:
Personal Use
- Ownership is usually easy to prove.
- You may take diagnostic or recovery actions freely.
- The main risk is exposing private information via unsafe online tools.
Corporate / Enterprise Use
- Authorization may be required before accessing encrypted archives.
- Internal policies may define who may attempt password recovery.
- Changes must be logged for compliance or audit trails.
Mixed Use / Shared Devices
- Multiple people may have partial access or shared storage roles.
- Documenting individual access events becomes extremely important.
- Policies similar to those outlined in ethical ways to handle your encrypted RAR files ↗️ apply.
💼 All-In-One Compliance-Friendly Access & Diagnostics
One of the biggest legal risks when working with encrypted archives is exposure — sending the archive to third-party cloud services, unknown web apps, or tools without established privacy frameworks. Even benign actions like uploading a corrupted encrypted archive to an online tool can be interpreted as data disclosure.
FileBrio Office Suite removes that exposure by keeping sensitive diagnostic steps offline:
- Local-only processing ensures no accidental uploads.
- Built-in metadata and structure inspection helps you plan safe actions.
- Modules align well with compliance expectations, offering clear insight into what the archive needs — repair, verification, or safe recovery.
This is especially helpful when managing organizational data where privacy requirements are strict and auditability matters.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
🔐 Password Issues vs. Legal Boundaries
If a password is forgotten, lost, or documented poorly, your response must remain within your legal rights and organizational rules. Password-related issues intersect with compliance in the following ways:
1. Password Mismatch Is Not Proof of Permission
A forgotten password is a technical barrier. Legal permission to access the archive is a separate requirement. The organization may require verification of ownership or a request to IT or compliance before attempting safe recovery.
2. Encrypted Headers Change the Visibility Landscape
When headers are encrypted, you cannot see filenames or metadata. This is intentional: it prevents unauthorized inference. Articles like why encrypted headers hide your protected RAR contents ↗️ illustrate how privacy features affect recovery expectations.
3. Password Reset Does Not Exist
You cannot “reset” a RAR password the way you would reset a login password. Articles such as why resets don’t apply to your encrypted RAR file ↗️ explain how encryption enforces boundaries. Legally, this reinforces the expectation that only the rightful owner may attempt recovery.
4. Documentation Protects You
If you ever need to justify your actions, documented proof that you accessed the archive as an authorized individual is key.
🚧 High-Risk Zones to Avoid (Even When Files Are Yours)
It is possible to violate privacy or compliance unintentionally even when dealing with your own archives. Some practices to avoid include:
- Uploading encrypted archives to unknown online tools.
- Using “password removal” websites that may store or inspect your files.
- Sharing partially accessible archives with third parties without proper authorization.
- Attempting high-risk repair operations on the only existing copy.
Related risk-focused resources such as reasons online tools fail to protect your private data ↗️ can help clarify the privacy implications.

📦 Storage, Privacy, and Jurisdiction Differences
Where your archive is stored affects the legal framework that governs it. Laws differ by region, and cloud storage companies operate under their own terms of service. Practical considerations include:
- Data retention policies of cloud providers
- Backup accessibility by administrators
- Accidental data exposure via shared folders
- Legal obligations for corporate retention and audit logging
Using offline tools avoids many jurisdictional uncertainties, especially when archives contain private or confidential information.
🛡️ Secure Offline Workflow for Sensitive Archives
When handling encrypted archives responsibly, offline workflows are often the safest path. FileBrio RAR Master supports that approach by ensuring that all actions — diagnostics, repair, and safe recovery attempts — remain local to your machine. This eliminates the concern that encrypted archives could be transmitted, cached, or inspected externally.
- Offline handling aligns with compliance policies that prohibit cloud uploads.
- Metadata visibility helps you determine next steps without risky experimentation.
- Support for both RAR4 and RAR5 archives ensures you maintain compatibility across legacy and modern data.
This fits well with privacy-focused considerations discussed in why offline tools keep your encrypted RAR data private ↗️.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
🪜 Best Practices for Safe, Responsible Archive Handling
Below is a high-level checklist of practices that reduce both legal and technical risk:
- Confirm ownership before performing any action.
- Document purpose and authorization, especially in organizations.
- Avoid cloud tools when working with encrypted archives.
- Keep operations offline and under your control.
- Inspect metadata before attempting any recovery or password action.
- Use copies of the archive for testing or diagnosis.
- Follow internal policy for sensitive or corporate archives.
Additional safety guidance is available in resources such as how to design a secure workflow for your encrypted files ↗️.
⚖️ Legal Reminder
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📚 See Also
- How to Document Ownership of Sensitive Encrypted Archives ↗️
- Resetting a RAR/WinRAR Password: Why Resets Don’t Exist and What Safe Options You Actually Have ↗️
- Unlocking Password-Protected RAR/WinRAR Archives: Safe Methods for Legitimate Access ↗️
- Ethical Use of Publicly Available Information When Designing Security Policies ↗️
- Bypass RAR Password: What Users Really Mean and How to Access Your Own Archives Safely ↗️
- Brute-Forcing a RAR/WinRAR Password? Legal Boundaries, Practical Limits, and Safe Use Cases ↗️