
How to Handle Damaged or Partially Corrupted RAR Archives Without Losing More Data
Discovering a damaged or partially corrupted RAR archive can be stressful, and quick reactions—repeated extractions, random tools, rushed repairs—often make the problem worse. A corrupted archive is fragile, and every action risks further damage.
Before doing anything, you need to understand what kind of issue you’re facing. Some archives have only minor sector problems; others may be missing segments, footer blocks, or recovery records. Encrypted headers can make diagnosis harder and require extra care.
This article outlines a simple, safety-first approach to handling corrupted RAR files: how to recognize different damage types, avoid irreversible mistakes, and understand how RAR features influence recovery. It also explains how private, offline tools can help you inspect your archive securely without exposing any data.
🧭 Navigation
🧩 Introduction
RAR archives are designed to be resilient, but they are not immune to corruption. A single missing byte in a header block, a truncated footer, or a damaged data span can cause extraction failures, “unexpected end of archive” alerts, CRC mismatches, or partial file output. Understanding whether your archive is slightly damaged, severely corrupted, or simply unreadable due to encryption is essential for avoiding further harm.
This is where many users make their first mistake: assuming all damage is the same and trying random repairs. In reality, your strategy depends on whether the damage affects metadata, header blocks, compressed chunks, or multi-volume synchronization. Before attempting anything, you should also distinguish whether the issue is related to actual structural corruption or falls under a different category such as encrypted headers or incorrect password symptoms, which behave differently. For more clarity, comparisons like how to tell if your RAR file is locked or damaged ↗️ can help separate these cases.
🧠 Identifying Early Symptoms of RAR Damage
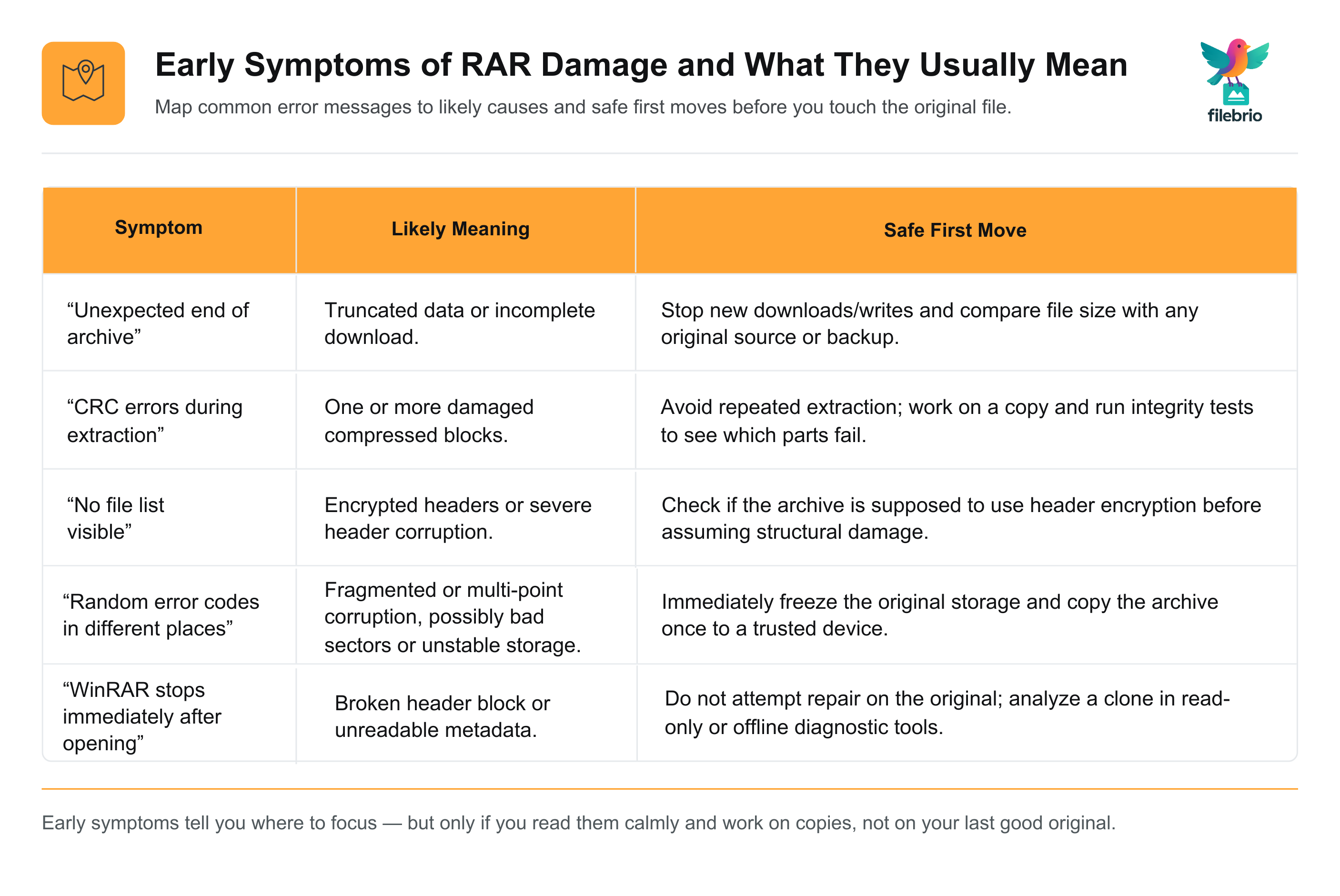
The simplest way to avoid making a corrupted archive worse is to accurately identify the early warning signs. Different symptoms reveal different failure points.
Here are common indicators and what they typically mean:
| Symptom | Likely Meaning |
|---|---|
| “Unexpected end of archive” | Truncated data or incomplete download |
| CRC errors during extraction | Damaged compressed block(s) |
| No file list visible | Encrypted headers or severe header corruption |
| Random error codes in different places | Fragmented or multi-point corruption |
| WinRAR stops immediately after opening | Broken header block or unreadable metadata |
Understanding these symptoms helps determine safe next steps. For example, “Unexpected end of archive” indicates a different situation than having no file list. Guides like what unexpected end errors mean ↗️ offer additional clarity on interpreting these alerts safely.
⚙️ Common Causes Behind RAR Corruption
Corruption rarely happens randomly. Most damaged RAR archives suffer from predictable triggers. Recognizing the cause helps you understand what might be salvageable.
-
- Interrupted downloads — especially from unstable servers.
- Faulty USB drives — removable media often fails silently.
- Hard drive bad sectors — physical degradation can affect compressed data.
- Cloud sync conflicts — syncing mid-write corrupts active archives.
- Power loss during extraction or creation.
- Damaged multi-volume chain — missing or out-of-order segments.
- Overwriting a partially downloaded file.
Some triggers are environmental. Others stem from storage behavior. Understanding these allows you to take the right precautions. Articles like why RAR archives become corrupted ↗️ provide deeper insights into preventative measures.
🛡️ A Secure Way to Understand What’s Really Broken
When a RAR archive starts showing symptoms like truncated data, missing segments, or CRC failures, it’s easy to panic and try everything at once — which often causes more damage. Before you touch the archive again, it helps to get a clear, offline-safe view of what’s actually intact.
To make analysis safer and more predictable, you can use tools that show structure without extracting anything:
- See whether damage is local or widespread before risking repairs
- Check header health and identify cases where corruption only affects metadata
- Confirm whether encrypted headers are involved so you don’t confuse damage with protection
- Review multi-volume layout to spot missing or misnumbered parts
| What You Usually See | What a Safe Diagnostic View Shows |
|---|---|
| “Unexpected end of archive” | Whether the tail is truncated and if early files are still intact |
| CRC failures on some files | Which compressed spans are damaged and which remain recoverable |
| No file list visible | Header corruption vs encrypted-header behavior |
| Volumes failing to load | Whether segments are missing, out of order, or mismatched |
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
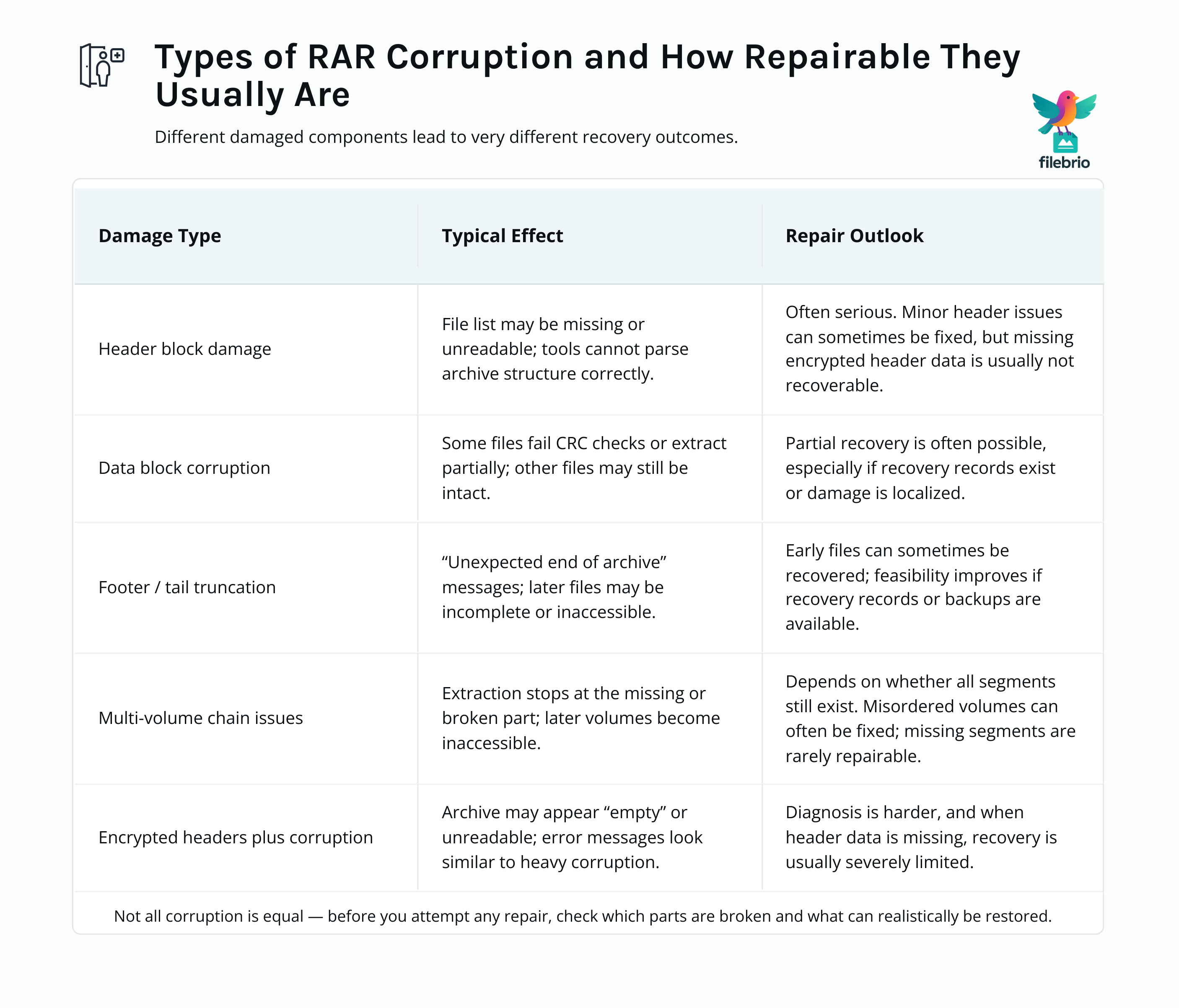
📁 How RAR Structure Breaks Under Corruption
RAR internally organizes data into blocks, headers, and compressed chunks. Not all corruption is equal. Depending on which component is damaged, feasibility varies significantly.
1. Header Block Damage
This prevents listing files, identifying compression method, or determining archive structure. It is one of the most serious forms of corruption.
2. Data Block Corruption
Individual files may fail CRC checks, but the rest of the archive could still be intact.
3. Footer / Recovery Block Damage
Truncation or last-sector corruption often causes “Unexpected end of archive” warnings.
4. Multi-Volume Sync Loss
A missing segment prevents extraction of all subsequent volumes.
5. Encrypted Header Interference
If a file appears corrupted but actually has encrypted headers, it behaves differently. Understanding this distinction is crucial, as explored in how encrypted headers hide your protected RAR contents ↗️.
🔍 Safe First Diagnostics (Without Making Damage Worse)
Here are safe, low-risk diagnostic steps you can perform immediately—without altering the archive or triggering further data loss.
- Always work on a copy of the archive. Never touch the original.
- Check the archive size. If it’s smaller than expected, it’s probably truncated.
- Compare nearby files. Adjacent archives or related items may hint at naming patterns or creation conditions.
- Open the archive read-only.
- Test archive integrity (non-repair mode).
- Check if headers are encrypted. This affects what information is visible.
At this stage, avoid any repair attempts. For deeper guidance, consider insights from how to safely diagnose your locked RAR file ↗️ which outlines safe approaches to initial checks.
🧩 What Can Be Repaired—and What Cannot
Not every damaged RAR archive is salvageable. Some forms of corruption are recoverable. Others are mathematically impossible to repair or reconstruct.
Here’s what typically can be repaired:
- Broken data blocks (partial recovery possible)
- Footer corruption with recovery records present
- Minor header inconsistencies
- Multi-volume issues if all segments exist but are misaligned
What cannot realistically be repaired:
- Missing encrypted header data
- Truncated multi-volume chains
- Files lost due to missing sectors in storage media
- Archives with nearly all metadata overwritten
Understanding feasibility is important before taking further steps. Articles like how to verify recoverability of your locked RAR file ↗️ provide deeper context for evaluating feasibility.
🛠️ Role of Recovery Records and .rev Volumes
RAR files may include built-in recovery records or external .rev volumes. These act as redundancy layers. They cannot fix everything, but they greatly increase the chance of restoration.
Recovery features help with:
- Correcting bit-level corruption
- Reconstructing small damaged sectors
- Rebuilding parts of missing data blocks
They cannot help with:
- Encrypted header damage
- Missing multi-volume segments
- Total truncation
To learn more, see how recovery records and .rev volumes help protect data ↗️.
📦 Multi-Volume Archives: Special Risks and Handling
Multi-volume RAR archives (.part1.rar, .part2.rar) are more fragile than single-volume ones because corruption in one segment affects all later segments.
Common multi-volume corruption scenarios:
- Missing segment — extraction stops entirely.
- Misnumbered segment — causes file-order confusion.
- Truncated later volumes — may produce CRC errors.
Handling multi-volume files safely requires preserving all pieces and avoiding overwriting. For more insights on multi-volume behavior, see understanding multi-volume RAR behavior ↗️.
🔐 A Private, Offline Way to Inspect and Protect Your Damaged Archive
Once you confirm the archive is corrupted — not just locked — the next challenge is choosing actions that won’t destroy what’s still recoverable. This is where having a fully local, privacy-first diagnostic environment becomes essential.
A proper offline workspace helps you:
- Inspect RAR4/RAR5 structure without exposing sensitive data anywhere online
- Evaluate feasibility before committing to any repair paths
- Check whether recovery records or .rev volumes are usable
- Separate encryption behavior from corruption so you don’t misinterpret errors
- Analyze multi-volume archives safely without risking accidental overwrites
| If You Act Blindly | If You Analyze Offline First |
|---|---|
| Risk overwriting the last intact data blocks | Work with a controlled copy while keeping the original untouched |
| Mix up multi-volume parts | See exactly which segments are missing or mismatched |
| Confuse encrypted headers with corruption | Identify the real cause before applying tools |
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
🔐 Encrypted Headers and Why They Complicate Damage
Encrypted headers significantly change how damage appears. A severely corrupted archive with plaintext headers still shows the file list. One with encrypted headers shows nothing.
Symptoms of encrypted header + damage combination:
- No file list even when archive is valid
- Error messages resembling corruption
- Archive appears “empty” in some tools
To understand this in detail, refer to how header encryption affects recoverability ↗️.
🛡️ Safe Handling Practices (Critical Do’s and Don’ts)
Do:
- Work strictly on a copy of the archive.
- Document all actions you take.
- Inspect file metadata without modification.
- Preserve original storage media when corruption is suspected.
Don’t:
- Extract repeatedly—this worsens damage.
- Use random third-party repair tools.
- Move the file between unstable storage devices.
- Rename multi-volume files before analysis.
These practices mirror broader safety principles in related workflows such as how to begin repairing a corrupted RAR file ↗️.

📘 How to Prevent Future RAR Corruption
Once you’ve dealt with a corrupted archive, it’s worth reinforcing your future storage habits:
- Use redundant backups across trusted media.
- Enable recovery records for critical archives.
- Avoid cloud-syncing active RAR files.
- Store important archives on stable storage devices.
- Test archives occasionally to ensure long-term health.
For additional insight, explore how to prevent RAR data loss across storage devices ↗️.
📎 Summary
Handling a damaged RAR archive requires precision, caution, and a solid understanding of how RAR structures behave under stress. Whether the issue stems from truncated data, header corruption, multi-volume broken chains, or missing recovery records, the key goal is to prevent further damage. By analyzing the archive carefully, avoiding risky extraction attempts, leveraging safe offline diagnostics, and understanding what can and cannot be repaired, you maximize your chances of preserving the data you still have.
⚖️ Legal Reminder
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📚 See Also
- What to Do When WinRAR Shows ‘Unexpected End of Archive’ ↗️
- How to Check the Internal Structure of RAR Archives Without Extracting Files ↗️
- How to Determine If a RAR Archive Uses Header Encryption ↗️
- Lost Your RAR/WinRAR Password? How to Assess Your Situation Before Taking Action ↗️
- Opening RAR/WinRAR Archives With or Without a Password: A Practical Guide to Safe Access Options ↗️
- Why Old RAR4 Archives Still Matter — and When to Convert Them ↗️
- How to Avoid Losing Access to Decade-Old RAR Archives ↗️