
Legal Boundaries for RAR/WinRAR Access Attempts — Safe Options for Verified Owners Only
You may have reached a point where every familiar password variation has failed. You own the RAR archive, you know the data inside belongs to you — yet the password is gone. In frustration, you search for phrases like “brute force RAR password,” “RAR password guesser,” or “RAR password attack.” What you’ll find online ranges from misleading to outright dangerous.
This expanded guide — now in deep, long-form detail — explains legal boundaries, cryptographic limits, safe use cases, ethical concerns, practical feasibility, diagnostic steps, memory-based strategies, hardware considerations, and the safest offline ways to examine your own encrypted archives without exposing them online.
🧭 Navigation
Important
The information provided in this article applies exclusively to RAR / WinRAR archives for which you have full, demonstrable ownership or properly documented authorization. If you are not the rightful owner of the data, do not directly control it, or cannot clearly prove permission to access it, you must stop immediately. Attempting to access, recover, or modify data without explicit authorization may violate criminal law, civil statutes, corporate compliance requirements, and privacy regulations in many jurisdictions. You alone are responsible for ensuring that your actions are lawful and properly permitted before proceeding.
⚡ TL;DR — Quick Summary
Brute-forcing a RAR password is extremely limited by cryptography, ethics, and legality. Modern RAR versions (especially RAR5) use heavy key-derivation functions and strong AES-256 encryption, making unrestricted guessing mathematically impossible for long or complex passwords. You may attempt recovery only on archives you fully own or have explicit permission to access.
Before attempting anything, you must:
- Diagnose the archive to determine whether the problem is password mismatch, corruption, or missing data.
- Evaluate feasibility using password length, complexity, and RAR version.
- Avoid uploading files to online “RAR password recovery” sites — they are unsafe and violate privacy.
- Use privacy-first offline analysis to safely determine next steps.
The safest real-world approach is not raw brute force but structured, privacy-preserving offline diagnostics and password reconstruction techniques.
🔍 Why Users Turn to “Brute-Force” — The Real Context
People rarely seek brute-force information without a legitimate need. Most cases involve:
- old backups from a previous computer,
- family photo archives encrypted years ago,
- legacy work files from earlier roles,
- client-delivered archives where documentation was misplaced,
- personal data protected with a password forgotten over time.
It’s important to acknowledge these are legitimate, valid scenarios. But to act responsibly, you need a safe workflow. Many users benefit from understanding how to evaluate your situation before taking action ↗️, which helps avoid rushed or risky attempts.
Most people mistakenly assume the archive is inaccessible due only to a password issue. But encrypted RAR failures may actually stem from corruption, damaged volumes, or format confusion — something that detailed diagnostics like those described in identifying password vs damage vs format issues ↗️ help clarify.
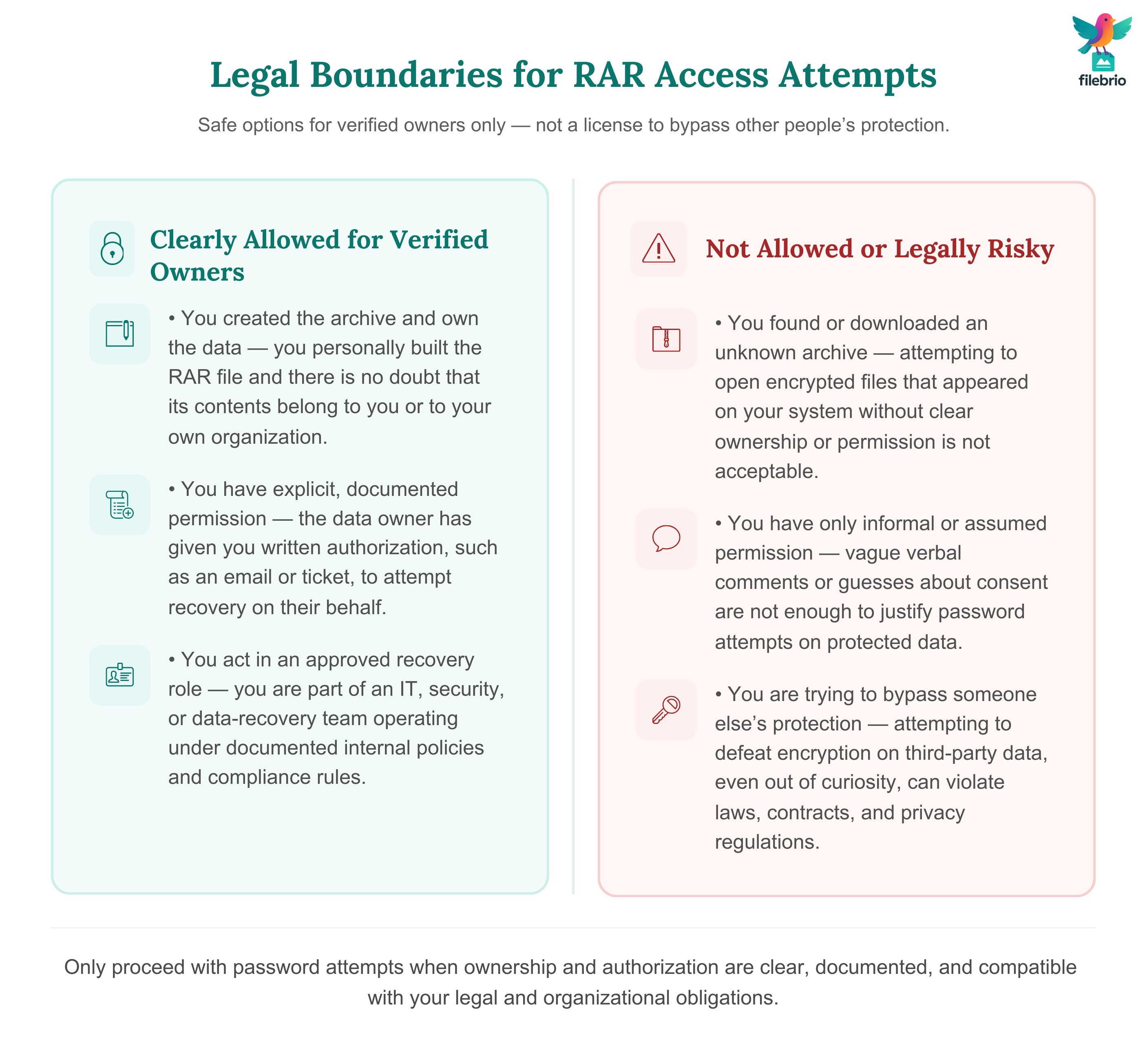
⚖️ Legal Boundaries: What’s Allowed and What Isn’t
Attempting to gain access to someone else’s encrypted files — even without malicious intent — violates digital access laws, workplace rules, and confidentiality agreements.
Safe and permissible scenarios include:
- You created the archive originally.
- You are the verified owner of the data.
- You serve in a compliance-approved IT or data-recovery role.
- You have written permission from the data owner.
For deeper clarity, many users benefit from reviewing how to ensure you’re recovering only RAR files you own ↗️ and ethical guidelines for working with password-protected files ↗️, especially for corporate or regulated environments.
Always document authorization. This protects you legally and ensures transparency.
⏱️ Practical, Mathematical & Cryptographic Limits
RAR encryption relies on real cryptographic constraints, not simple obfuscation. Understanding these limits is crucial before attempting any form of password enumeration.
RAR4 vs RAR5: Why It Matters
RAR4 uses a faster key schedule and AES-128, while RAR5 uses:
- AES-256 encryption
- A very heavy key-derivation function (KDF) designed to slow down password attempts
- Optional encrypted headers that hide filenames and metadata
If your archive uses RAR5, the effective guessing rate can drop dramatically — one reason RAR5’s KDF plays such a large security role ↗️.
Why Even Powerful GPUs Struggle
Online myths exaggerate GPU capabilities. In reality, RAR5’s KDF significantly slows down even high-end hardware. The difference between theoretical speed and actual speed can be dramatic — an insight explored in GPU acceleration and real-world RAR password limits ↗️.
The Exponential Nature of Password Space
Password entropy grows exponentially. A small difference in length or symbol count can change a 2-hour job into a 200-year one.
Understanding entropy through explanations like password length & entropy ↗️ helps users identify realistic vs impossible scenarios.
Header Encryption Makes Recovery Harder
Header encryption removes filenames, sizes, and hints, reducing contextual clues. To determine whether your archive uses this feature, refer to how to check header encryption ↗️.
🧰 All-In-One Offline Solution
Before considering brute force or memory reconstruction, you need a safe, private offline environment that lets you analyze the archive without risk.
FileBrio RAR Master acts as an all-in-one toolkit ↗️ with:
- RAR4 & RAR5 detection
- Metadata and structural inspection
- Archive corruption checks
- Header encryption detection
- Safe feasibility estimation
- GPU-supported recovery in legal use cases
You can install it from the official FileBrio Office Suite download page ↗️.
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — part of the FileBrio Office Suite — is a privacy-first, offline Windows toolkit for diagnosing and safely regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives.
- Local processing only — nothing leaves your PC.
- Smart diagnostics to separate password issues from corruption.
- Owner-verified recovery workflows designed strictly for legitimate use.
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master may be used only with archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. It performs all analysis and recovery operations locally on your device, without uploading data anywhere.
________________________
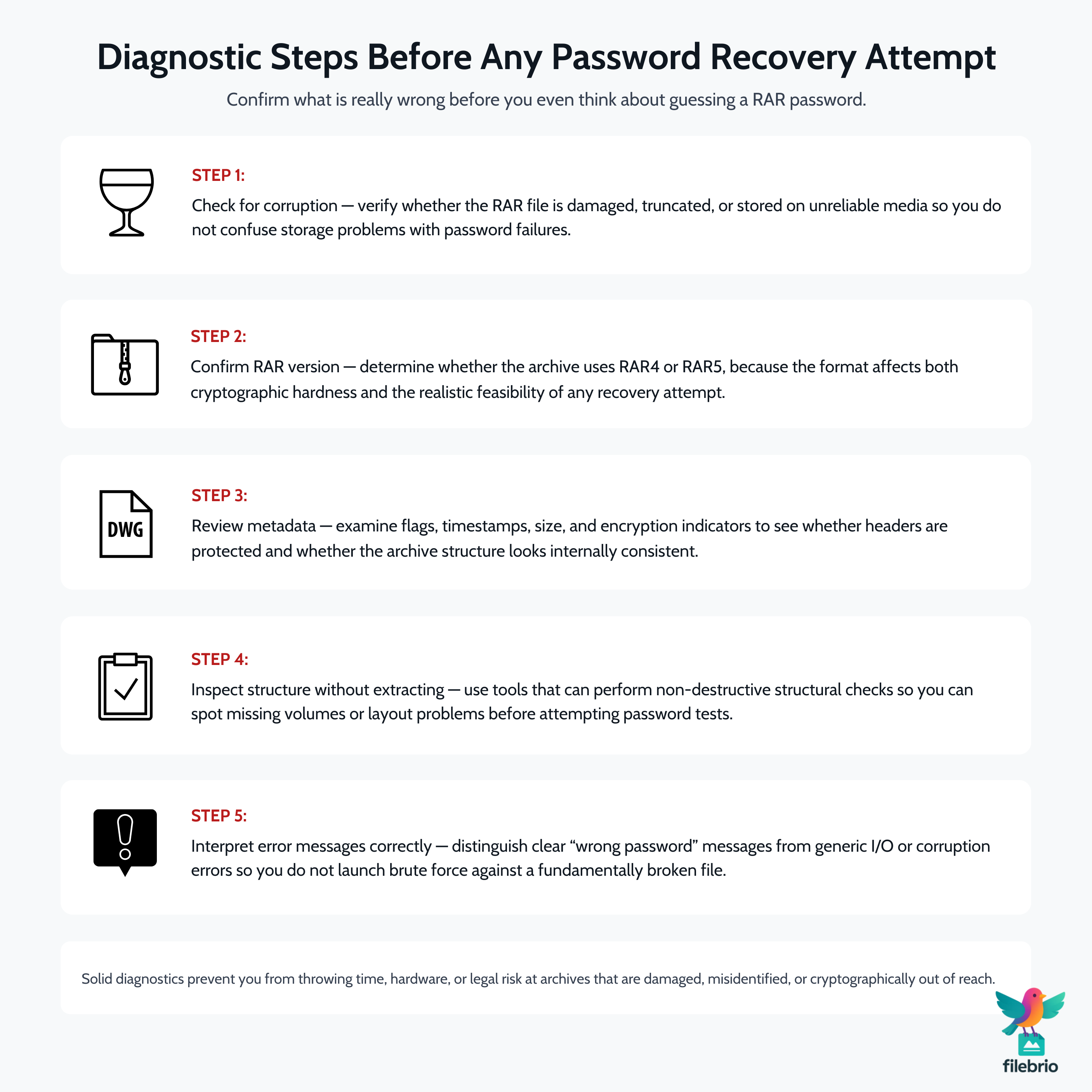
🔎 Diagnostic Steps Before Any Password Recovery Attempt
Most users waste effort attempting brute-force when the root issue is something else entirely. Proper diagnostics prevent wasted time and avoid risks.
1. Check for Corruption
Many RAR files fail due to corruption, not passwords. Guidance such as how to handle damaged RAR archives ↗️ helps ensure you don’t worsen damage.
2. Confirm RAR Version
RAR4 vs RAR5 drastically changes feasibility. RAR5 is far heavier and usually less recoverable without strong contextual clues.
3. Review Metadata
Metadata provides clues about feasibility. For example, reading RAR metadata ↗️ can reveal encryption flags, header status, or structural issues.
4. Inspect Structure Without Extracting
Tools that allow non-destructive structure inspection — as shown in how to inspect internal structure safely ↗️ — help build a recovery plan before any guessing attempt.
5. Interpret Error Messages
Some failures clearly indicate password mismatch; others indicate corruption. Understanding RAR error messages ↗️ helps differentiate these.
🧠 How Password Behavior, Length & Entropy Shape Feasibility
Brute-force feasibility is not only about computing power. It’s about human behavior: how passwords were created, recalled, and forgotten.
Helpful insights can be found in psychological patterns behind forgotten RAR passwords ↗️, which show why memory fades and how people unconsciously follow predictable creation habits.
Why Length Matters More Than Anything
Even a simple pattern becomes extremely strong once length increases. An 8-character mixed password may be borderline feasible; a 12-character password is realistically beyond reach in most cases.
Character Set Expansion
Adding numbers, symbols, or Unicode expands the search space drastically. As covered in RAR password encoding considerations ↗️, multilingual scripts also alter behavior and compatibility.
Passphrases
Even simple English passphrases such as four words often become infeasible unless you have clues or structural hints.
🔡 Human Password Patterns vs Cryptographic Reality
People rarely create passwords randomly. They follow:
- naming conventions,
- personal habits,
- date-based structures,
- repeated symbols,
- keyboard patterns.
This is why tools like naming convention analysis ↗️ and studying your password creation style ↗️ are often more valuable than brute force.
Reducing the possible pattern space is the only realistic way brute-force ever becomes feasible.
🧩 Structured Memory Reconstruction Methods
Pure brute force is almost never the winning strategy. Memory reconstruction is often far more effective.
Some proven techniques include:
- memory triggers (reconstructing a lost password using memory cues ↗️)
- contextual associations (where, why, and when the archive was created)
- examining nearby files or folder names
- evaluating how you created passwords during that time period
- checking old devices, notes, or synced password stores
Users are often surprised by how far contextual reflection and structured memory exercises can reduce guesswork.

❗ Common Misconceptions & Dangerous Mistakes
“I’ll upload my archive to an online brute-force website.”
This is extremely dangerous. These sites often store your archive permanently. See why online brute-force sites are unsafe ↗️.
“Any file can be opened eventually.”
No. RAR5 with a strong password is mathematically unopenable within human timescales.
“I’ll try random guesses manually.”
Random manual guessing is ineffective and may cause confusion or repeated attempts masking diagnostic clues.
“Quick recovery tools can instantly break RAR files.”
Instant recovery is not possible unless the password is short or highly predictable. Many tools exaggerate their capabilities.
🔒 Secure Offline Recovery (2/3 Commercial Block)
When privacy, legality, and data protection matter, an offline workflow is essential. Never upload encrypted archives or attempt online cracking methods.
To better understand why offline handling matters, review the comparison of online vs offline recovery ↗️.
FileBrio RAR Master supports:
- Local-only diagnostics
- Controlled GPU-assisted recovery (within legal limitations)
- Feasibility estimation via the password time-to-recover estimator ↗️
- Metadata analysis & structural inspection
- Responsible-use guidelines through official support & legal documentation ↗️
________________________
FileBrio RAR Master — a secure, offline Windows toolkit for regaining access to your own password-protected RAR / WinRAR archives while keeping all data strictly on your device.
- Offline-only processing — never uploads your archives.
- Smart issue detection — password vs corruption.
- Fast recovery workflow optimized for legitimate ownership.
⬇️ Download FileBrio RAR Master
Reminder: FileBrio RAR Master is intended only for archives you own or are explicitly authorized to access. All operations run locally on your PC.
________________________
⚖️ Legal Reminder
This article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only. Any examples, scenarios, or references to password recovery, archive security, or related tools (including FileBrio RAR Master or similar software) are intended solely to help you better understand how to protect and manage your own data.
You may only apply any techniques, workflows, or tools described here to files and archives that you fully own or are explicitly and verifiably authorized to access. Attempting to bypass, remove, or recover passwords for third-party data without clear permission may violate criminal law, civil law, or internal company policies in your jurisdiction.
Nothing in this article constitutes legal advice. Laws and regulations differ between countries and organizations, and you are solely responsible for ensuring that your actions comply with all applicable legislation, contracts, and internal policies. If you are unsure whether a particular action is lawful or permitted, consult a qualified legal professional before proceeding.
📘 Summary & Next Steps
Attempting to brute-force a RAR password is not about hacking — it is about understanding legal constraints, cryptographic limits, and ethical responsibilities. Many archives cannot be recovered through brute force alone due to strong AES-256 encryption and heavy RAR5 KDF hardening.
Your safest path forward:
- Diagnose the archive properly.
- Determine whether corruption or header encryption is involved.
- Perform feasibility assessments using length, entropy, and password patterns.
- Use structured memory reconstruction to reduce guess space.
- Follow privacy-first, offline workflows.
- Use secure tools that never upload or expose your data.
When handled correctly, many users regain access to their own archives safely, ethically, and with full control over their data.
📚 See Also
- When It Makes Sense to Attempt Password Recovery — And When It’s Mathematically Unopenable ↗️
- RAR Security Explained: Why Your Password Can’t Be Reset ↗️
- GPU Acceleration in Password Guessing: Benefits, Limits, and Safety Considerations ↗️
- How to Understand Password Guessing Time Estimates ↗️
- Why Online RAR Password Tools Fail — and What Legitimate Users Can Do Instead ↗️